If your organization deals with sensitive information relating to patients’ health data, complying with HIPAA rules is a must. This is especially true if you’re using databases to store and manage such information.
What is HIPAA?
HIPAA — or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 — is a federal law that functions to protect health information.

This includes everything from personally identifiable data to insurance, billing, and clinical care data.
HIPAA’s main goal is to improve information sharing while protecting the privacy and security of health information.
Ultimately, it aims to improve the quality of the US healthcare system. Entities required to comply with HIPAA rules include:
- Hospitals
- Medical services providers
- Employer-sponsored health plans
- Research facilities
- Insurance companies
- Associates of the above-listed entities
What are HIPAA Compliance Requirements?
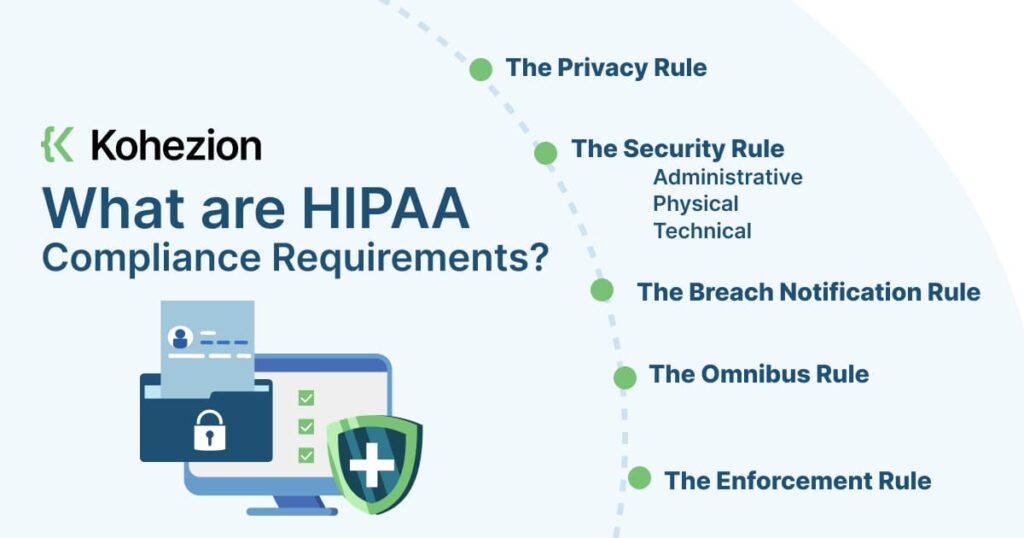
HIPPA compliance has five primary rules that entities must follow. These are:
- The Privacy Rule: this rule establishes patients’ right to privacy and private information. It also sets up the framework for what’s considered to be protected health information (PHI). PHI can be anything from past, present, or future documentation of physical or mental conditions to records referencing past, present, or future healthcare payments. Covered entities can only disclose PHI during highly specific care, legal, or research situations — these can be extremely narrow situations and subject to court interpretation.
- The Security Rule: this rule establishes the national standards for protecting PHI data. These standards extend across various aspects of the entity, including their technology, administration, and hardware. These controls may fall into the category of:
- Administrative: this includes policies and processes that impact PHI. This also covers aspects of healthcare administration, such as HR and employee training.
- Physical: this refers to physical safeguards that reinforce secure access to physical equipment containing patient data. Such equipment includes computers, routers, switches, and data storage.
- Technical: this refers to cybersecurity elements such as computers, mobile devices, network security, encryption, and device security.
- The Breach Notification Rule: this rule defines what happens if and when a security breach occurs. If a breach occurs, the entity must do the following:
- Notify the people impacted by the breach in a formal, written notice either by mail or email.
- If the entity doesn’t have contact with more than 10 people in the breach, they must provide alternative notice, such as a website posting or notice in major news sources.
- The entity must provide the notice no later than 60 days from the breach discovery.
- If the breach affects over 500 people, the entity must provide prominent public notice through media outlets.
- For breaches affecting over 500 people, the entity must also notify the Secretary of Health within 60 days. If less than 500 people are affected, the entity must notify the Secretary by the year’s end.
- The Omnibus Rule: this rule expands the reach of the law to organizations outside of entities (hospitals, service providers, etc). This means that covered entities are responsible for violations committed by their business associates. They must also update their risk assessments, gap analysis, and compliance procedures according to this rule.
- The Enforcement Rule: this rule defines guidelines for investigations and penalties for violations of security and privacy rules. This also establishes procedures for responding to complaints and investigating alleged violations.
Are Databases HIPAA Complaint?
Databases aren’t inherently HIPAA-compliant.
However, if you’re using systems and processes that use databases to manage healthcare information, your database must be compliant with regulations. This means considering aspects such as access control, encryption, audit trails, backups, and recovery.
Benefits of HIPAA Compliance
Adhering to HIPAA rules isn’t only about compliance for compliance’s sake. It doesn’t only make you safe from possible regulatory penalties; it also gives you the following benefits:

Protection Against Data Loss
PHI loss is a serious offense, and HIPAA compliance ensures this doesn’t happen to your organization. You avoid putting sensitive data at risk through standards such as encryption and authentication.
To protect data, data encryption transforms data into a coded format that only authorized personnel can access with a decryption code or key.
With encryption, data becomes unreadable and inaccessible to criminals — even if they successfully steal it. Encryption is required by the Security Rule for all PHI-related data.
Meanwhile, authentication verifies the user’s identity accessing the database and protects the healthcare data.
This ensures that only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive patient data. Examples of authentication methods are automatic log-off or strong authentication, which include two-factor authentication.
Increased Customer Trust and Loyalty
Being HIPAA-compliant helps you earn customers’ trust and loyalty.
The implementation of safeguards that ensure the confidentiality and integrity of PHI shows your patients and clients that you’re taking PHI protection seriously.
This also leads to increased loyalty. When a patient or a client knows they can trust your organization to handle their data safely, they’re more likely to continue partnering with you for their needs.
This also means you’ll need fewer resources invested in attracting new patients and clients, increasing your profitability.
Reduced Liability
HIPAA doesn’t only protect patient data; it also protects your organization and staff. For instance, implementing mandatory HIPAA training means you’re better protected in case of a lawsuit or investigation.
Not providing adequate HIPAA training could lead to hefty penalties and personal liability lawsuits for your executives. However, with HIPAA compliance and training, you reduce the likelihood of errors.
Avoiding errors in medical records improves the overall safety and quality of patient data protection. You can then achieve greater operational efficiency while also reducing liabilities dramatically.
Enhanced Cybersecurity
With HIPAA compliance, your organization must keep your data systems, networks, and software updated at all times. Previously, medical providers failed to keep their systems updated — if one exists at all.
Meanwhile, complying with HIPAA regulations forces your organization to be aware of malicious software that can adversely affect PHI. You prevent record breaches when you put adequate cybersecurity measures in place.
Patient Safety Culture Development
Fostering a safe and secure patient culture is a must if your organization deals with sensitive patient data. Adhering to HIPAA regulations results in a patient-centric culture.
Safeguarding patient data has positive effects on aspects of healthcare such as fall prevention, infection control, and overall medical safety. When your staff follows HIPAA procedures correctly, you minimize the chance of errors.
Subsequently, you ensure the safety of patients’ personal and medical records, which should remain private and secure. Fostering this culture gives your organization access to the necessary tools and knowledge for PHI safety and protection.
How to Build a HIPAA-Compliant Database
Creating a HIPAA-compliant database revolves around ensuring data security and continuous monitoring. The following steps will help you build such a database with relative ease:
1. Create a HIPAA Compliance Strategy
Creating a HIPAA compliance strategy ensures your database meets requirements by the law, particularly if it contains PHI.
That means any patient information you handle is free from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Take the following steps to create a HIPAA compliance database strategy:
- Conduct a risk analysis to identify potential PHI risks.
- Implement physical, technical, and administrative safeguards. This may include network and device data encryption, access control, and backup system creation.
- Train employees on HIPAA compliance policies and procedures. This includes learning to identify and react to security risks.
- Regularly review and update policies and procedures. Ensuring everything is up to date with HIPAA regulations.
- Monitor access to the database and conduct audits. Look for any unauthorized access or use of PHI.
- Create and test a contingency plan for security breaches.
2. Identify PHI
To identify a set of protected health information (PHI) for a HIPAA-compliant database, follow these steps:
- Determine Your Database’s Scope: this includes any electronic PHI created, received, or transmitted to your organization.
- Identify Covered Entities: determine if you’re a covered entity under HIPAA. You’re a covered entity if you’re a healthcare provider, healthcare clearinghouses, or a business associate providing services for a covered entity.
- Determine PHI Types: this may include names, addresses, dates of birth, social security numbers, device identifiers, email addresses, biometrics, lab or imaging results, medical histories, and payment information.
- Limit Access: implement access controls to sensitive details to protect your database. Use user authentication to ensure all those who have access to the data are authorized personnel.
- Ensure HIPAA Compliance: follow the private, security, breach notification, omnibus, and enforcement rules. If you’re developing an app or another type of product, know what HIPAA will require in terms of security controls and specific workflows.
3. Implement Safeguards
To ensure PHI security, implement the following safeguards:
- Physical Safeguards: this includes limiting physical access to facilities to only those who have proper authorization. It also includes implementing device access controls.
- Technical Safeguards: this includes authentication, transmission security, digital security, and verification. This also covers app architecture, data safeguards, systems integrity, and push notification formatting.
- Administrative Safeguards: this includes access controls, audit controls, integrity controls, information access management, and workforce training, management, and evaluation.
4. Implement Access Controls
Access controls limit access to PHI and other sensitive details to authorized personnel only. You can achieve this through various methods and best practices such as:
- Unique user identification
- Automatic log-off
- Emergency access
- Encryption
- Strong authentication
- Access monitoring
All of these are must-haves for healthcare apps. Also, analyze app activity logs to identify unauthorized access or attempts.
As much as possible, practice data minimization — collect only the most necessary information for the task. This limits potential vulnerabilities to the security system and maintains the confidentiality of patient data.
5. Maintain Information Securely
When maintaining information on a HIPAA-compliant database, follow technical requirements and best practices such as:
- Use encryption when storing production and staging assets
- Limit access to sensitive patient details
- Host PHI on servers with a signed Business Associate Agreement
- Practice data minimization
Again, continuous monitoring and updating of security systems is a must. Identify current and future threats and deploy real-time alert mechanisms.
On top of that, invest in state-of-the-art encryption models and enforce policies that enable an organization-wide security culture.
6. Create Backup and Disaster Recovery Policies
Track and manage data and deploy policies around backup and disaster recovery.
Conduct regular checks on backup, and record data recovery exercises to identify areas of improvement. Make future projections based on such policies. Create audit logs to detect possible threats and flag issues in real-time.
7. Dispose of Any Unnecessary Information
When disposing of information in a HIPAA-compliant database, use secure file-wiping mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
Electronic PHI should be completely overwritten, purged, and deleted in all forms (including backups).
Pro tip: cloud storage providers such as AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure are familiar with HIPAA and can host electronic PHI with a signed Business Associate Agreement. This makes data wiping easier when disposing of unnecessary information.
8. Give Patients Access to Their Information
To ensure your database is 100% compliant, it’s wise to give patients access to their information. Follow these steps:
- Create a secure online portal. Patients can log in to this portal to access their information.
- Follow best practices. The portal should have features such as unique user identification, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access monitoring.
- Limit access. Leverage authentication to ensure only authorized users can view and access their data.
- Offer patient education materials. Provide patients with engagement tools to improve satisfaction and retention.
- Customize data fields. Use a custom solution that meets your needs.
- Comply with HIPAA rules as described above.
These steps give your patients 24-hour access to their health information while still adhering to HIPAA rules.
Use HIPAA Compliant Software When Building a Database
Using HIPAA-compliant software when creating a HIPAA-compliant database protects patients' privacy and prevents costly breaches and lawsuits.
Non-compliant software puts patient information at risk of being accessed or shared without proper authorization, leading to violations of HIPAA regulations.
On the other hand, HIPAA-compliant software ensures that administrative, physical, and technical safeguards are in place to secure and protect patient data.
Examples of HIPAA-compliant software for creating a compliant database include Kohezion.
Cloud vendors and health app developers also must implement the HIPAA Security Rule to ensure their software is compliant.
Build a HIPAA-Compliant Database with Kohezion
HIPAA-compliant databases should ensure the security and confidentiality of PHI. implementing such a database involves strategic steps and adherence to guidelines.

The benefits of complying with HIPAA rules extend beyond regulatory requirements; they also foster customer trust, reduce liability, enhance cybersecurity, and improve overall patient safety.
Kohezion is a robust cloud database platform that securely stores and manages PHI and HIPAA data. It’s easy to use since it’s a low-code database that you can master quickly.
Also, Kohezion offers quick turnaround times — it has the right tools that let you build your own tools for HIPAA compliance. Try Kohezion today and create your HIPAA-compliant database with ease.


