Interesting fact: your medical records, and any related data, are now worth more to hackers than your credit card data is.
This post offers a detailed guide to help you meet all necessary standards, ensuring that your practice is fully compliant and your patient data is secure.
We'll buid your first application for you. At no extra cost.
Let us build your first business application for free. Go from an idea to an application in under 2 weeks.

What is HIPAA compliance
HIPAA compliance means fulfilling the requirements of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. The legislation aims to protect patient privacy and ensure the security of Protected Health Information (PHI). The act delineates physical, administrative, and technical safeguards to which healthcare providers, insurance companies, and their business partners must adhere.
"HIPAA has helped to streamline administrative healthcare functions, improve efficiency in the healthcare industry, and ensure that protected health information is shared securely." - Steve Adler, HIPAA Journal
Being HIPAA compliant means demonstrating a commitment to patient privacy and the responsible management of their health information. That’s why 99% of organizations believe HIPAA compliance is important to their business.
Who Does HIPPA Compliance Apply To?
HIPAA compliance applies to a range of entities within the healthcare ecosystem. The groups obligated to adhere to HIPAA regulations are known as covered entities and business associates.
What Are Covered Entities?
Covered Entities form the backbone of the HIPAA regulatory structure. They are the healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses that handle Protected Health Information (PHI) directly.
These entities must implement privacy protections, conduct regular personnel training, and follow detailed procedures to manage PHI securely and responsibly. They're also responsible for reporting any HIPAA violations and could face fines from the Office for Civil Rights in case of non-compliance.
What Are Business Associates?
Business Associates are essential partners who perform functions involving using or disclosing PHI for a covered entity. These include consultants, legal advisors, IT specialists, billing companies, cloud storage providers, and email encryption services. They're not typically healthcare providers, but their role is critical in the HIPAA compliance ecosystem.
Business Associates must sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with the Covered Entity. This agreement outlines permitted PHI uses, safeguarding responsibilities, and the requirement to return or destroy PHI post-engagement. Business Associates must rigorously follow HIPAA's Privacy and Security Rules.
Are There Any Exceptions?
Yes, there are special cases where HIPAA rules don't apply. For instance, the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) may decide not to penalize non-compliance during emergencies (like with COVID-19 testing sites) if those involved act in good faith. This leeway is temporary and lasts as long as there is a public health emergency.
Also, organizations that only work with healthcare plans and clearinghouse functions and don't deal with protected health information (PHI) for other reasons might be exempt. These exceptions are only valid under particular conditions and don't fully exempt entities from following HIPAA rules.
Entities should regularly check the regulations and seek advice from legal experts in HIPAA law to understand the exceptions fully.
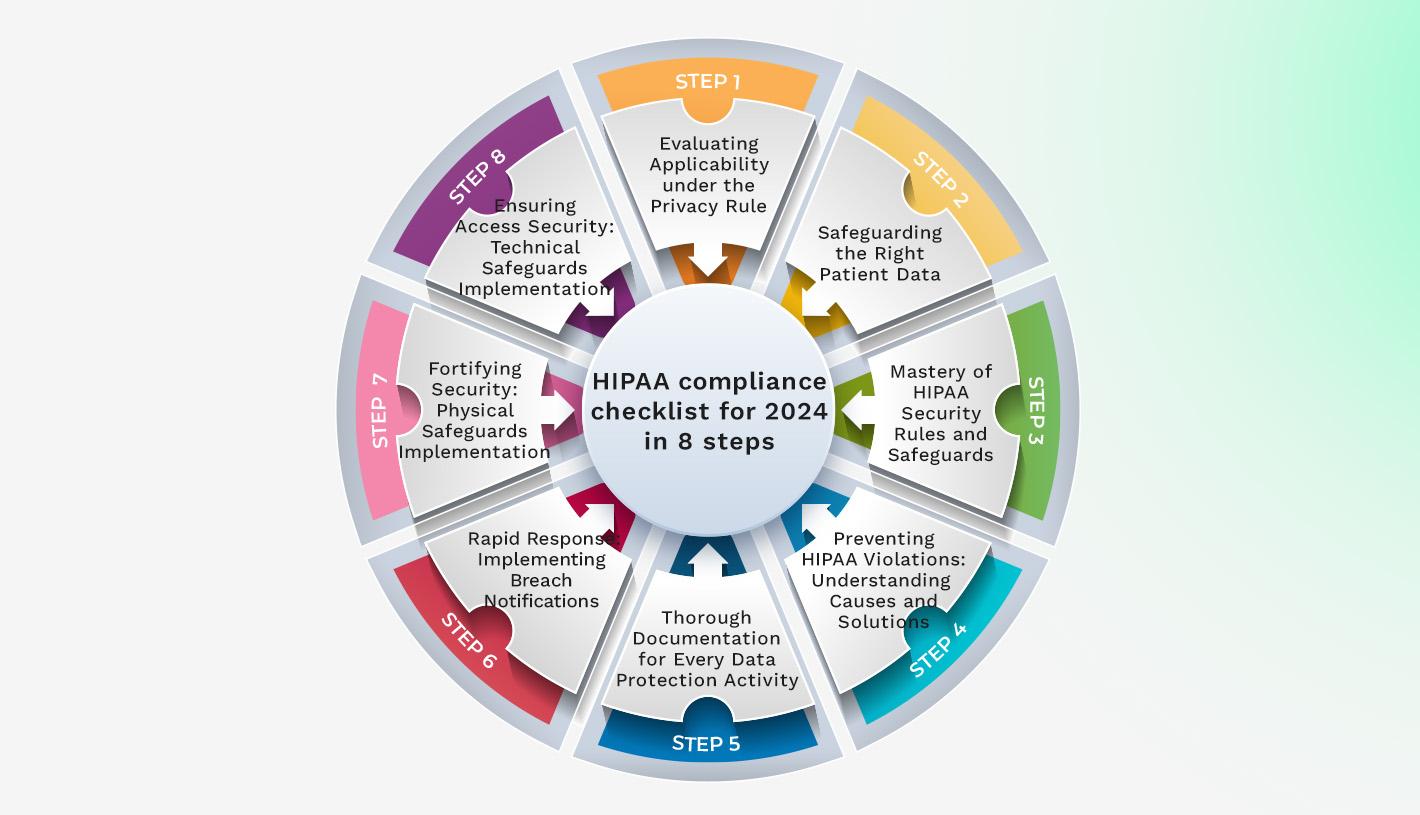
HIPAA compliance checklist for 2024 in 8 steps
Below is our HIPAA compliance checklist for 2024, broken down into eight simple steps. The checklist outlines the actions your organization must take to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations this year.
1. Evaluating Applicability under the Privacy Rule
Review your operations against the definitions of a Covered Entity or a Business Associate to determine if HIPAA's Privacy Rule applies to your organization. The rule applies to anyone who handles, possesses, or transmits PHI. Compliance with the Privacy Rule is obligatory if your organization falls into these categories.
Evaluate the types of health information you manage, and then document your status related to HIPAA standards. This first step ensures the rest of your compliance efforts are built on a solid foundation. Getting this step right will prevent potential issues.
2. Safeguarding the Right Patient Data
Identify what constitutes PHI. This includes any information in medical records, conversations about care or treatment, billing information, and any data that can be used to identify an individual. Then, take stock of where this information is stored, whether in digital systems, paper files, or with third parties.
Implement appropriate measures to guard against unauthorized access or disclosures. This includes employee training, using secure communication channels, ensuring encrypted data, and having proper contingency plans.
3. Mastery of HIPAA Security Rules and Safeguards
The HIPAA Security Rule has three safeguard categories: technical, physical, and administrative. These categories protect electronic PHI (ePHI) from threats and unauthorized access.
Technical Safeguards focus on the technology used to protect ePHI and control access to it. Think encryption, access controls, and audit logs.
Physical Safeguards are about securing the physical premises and hardware where ePHI is stored. This encompasses limited facility access, workstation use guidelines, and device and media controls.
Administrative Safeguards require formal policies and procedures for selecting, developing, and executing security measures to protect ePHI and manage the workforce's conduct.
Becoming proficient with these will require significant attention to detail and regular review to stay current with the evolving landscape of security threats and technologies.
4. Preventing HIPAA Violations: Understanding Causes and Solutions
Preventing HIPAA violations starts with understanding the common pitfalls that can lead to breaches. These include theft of equipment storing PHI, unauthorized access due to hacking, malware, or ransomware, physical breaches like office break-ins, misdirected communications containing PHI, casual discussions about PHI in public areas, and inadvertent posts of PHI on social media.
Most HIPAA breaches are often a result of internal mistakes rather than external threats. That’s why workstation security is key. For example, leaving a device unlocked with PHI on display can lead to violations. Also, ensure your software, including email and office suites, is properly configured. If PHI is encrypted per HIPAA standards, you're better protected in the event of theft or loss.
Organizations need comprehensive training, clear policies, and technology tools to prevent these violations. Any violation must be swiftly addressed with an investigation, remedial actions, breach notification, and policy adjustments to prevent a recurrence.
5. Thorough Documentation for Every Data Protection Activity
Solid documentation proves your due diligence and provides a blueprint for managing PHI that staff members can follow. Document every data protection activity, from authorized staff training schedules to implementing your security measures.
Your records should include policy manuals and procedural documents, training logs and materials provided to staff, security risk assessments and incident response plans, Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), records of PHI accesses, disclosures, audits, as well as maintenance, disposal, and data breach response records.
This documentation is your defense during an audit and a metric to gauge your compliance progression. Review and update these documents as regulations evolve or new threats emerge.
6. Rapid Response: Implementing Breach Notifications
The HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR) looked into 5,150 healthcare data breaches over the past ten years. In 2023, the number of data breaches doubled compared to 2018.
Under the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule, organizations must have a process for alerting individuals affected by a data breach. Notify the affected patients immediately and no later than 60 days after discovering the breach. Be sure to provide all the details about the breach, including what happened, the types of PHI involved, the steps individuals should take to protect themselves, and the measures you're taking to address the breach and prevent future occurrences.
In cases involving more than 500 patients, additional steps include notifying major media outlets and the Secretary of HHS. When breaches involve less than 500 people, log and report them annually to HHS.
Develop a breach notification policy that includes template notifications and outlines the process for managing the breach from discovery to resolution. Regularly train your staff on the policy so they're ready to act should a breach occur.
7. Fortifying Security: Physical Safeguards Implementation
Implementing robust physical safeguards protects your facility and the devices housing ePHI from unauthorized access and interference.
Ensure that only authorized personnel have access to areas where ePHI is stored. This involves secure keycard access, visitor sign-in protocols, and staff access levels. Develop clear policies on the proper use and physical security of workstations that access ePHI. Think about screen guards, auto-lock settings, and positioning away from public view.
Have processes for the handling and disposing of devices and media containing ePHI. Encrypt data on all devices, implement proper disposal methods for obsolete devices, and follow a strict protocol for data transfer. Consider surveillance systems to monitor areas where ePHI is accessed or stored. This deters unauthorized access and provides a record of activity should an incident occur. Keep detailed records of repairs and modifications to the physical components of your secure areas, such as doors, locks, and security systems.
These safeguards help prevent breaches and enable you to respond effectively should one occur.
8. Ensuring Access Security: Technical Safeguards Implementation
Ensuring access security with technical safeguards means implementing measures that protect the electronic systems and the ePHI they handle from unauthorized access.
Assign user IDs to all employees to limit their access to the necessary ePHI for their role. Introduce procedures for obtaining emergency access to ePHI when needed. Put mechanisms in place to verify that ePHI has not been altered or destroyed in an unauthorized manner. This could include digital signatures or checksums.
Encrypt ePHI when transmitted over networks outside your secure internal network. Ensure that the encryption is compliant with NIST standards. Implement hardware, software, and procedural mechanisms that record and examine activity in information systems containing or using ePHI.
Establish electronic procedures that terminate an electronic session after a predetermined time of inactivity to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. Construct mechanisms for data integrity, such as redundancy checking or version control systems, to ensure ePHI is not improperly altered without detection.
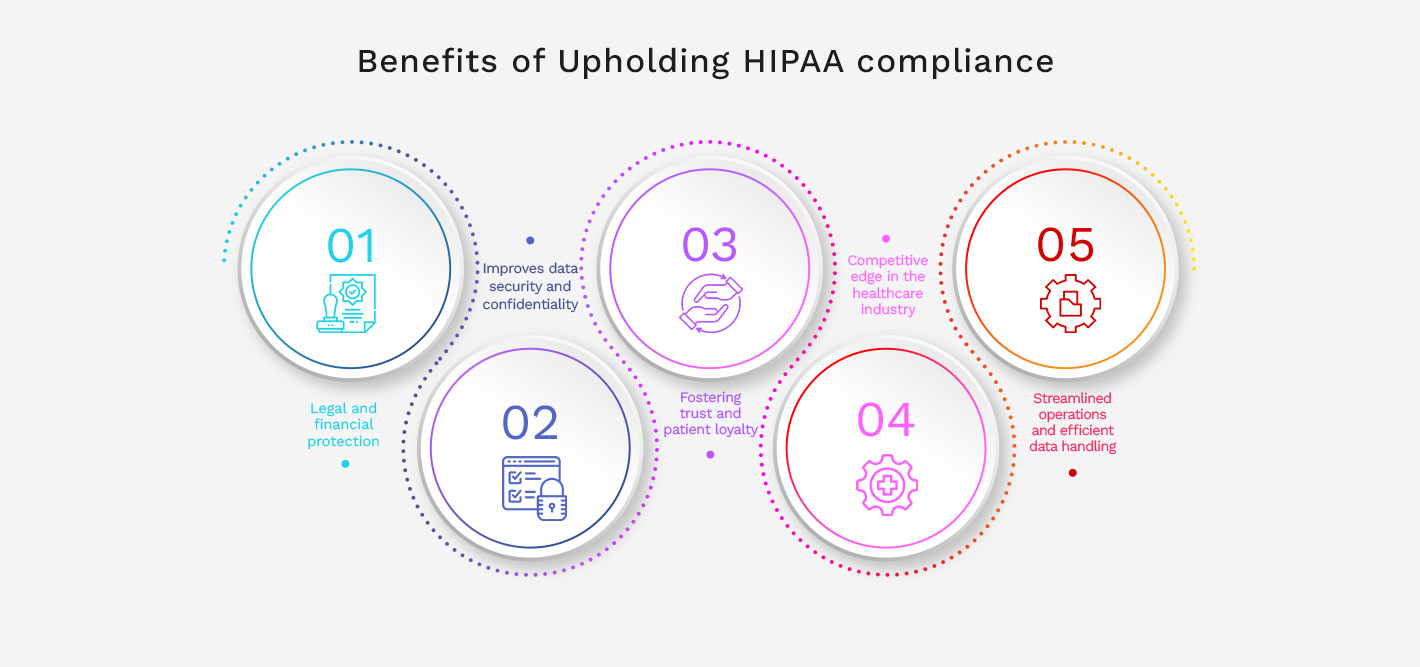
Benefits of Upholding HIPAA compliance
In this section, we'll outline how adhering to HIPAA regulations can safeguard patient information, build trust with clients, and avoid costly penalties for healthcare organizations.
Legal and financial protection
Upholding HIPAA compliance offers substantial legal and financial protection to your organization. Adhering to HIPAA standards helps you minimize the risk of legal battles resulting from data breaches and fines resulting from non-compliance issues. Criminal penalties for HIPAA violations can range from $50,000 to $250,000, depending on the severity of the violation. Civil fines for HIPAA breaches can vary from $100 to $1,500,000 per violation.
Improves data security and confidentiality
Implementing encryption, conducting regular risk assessments, and ensuring only authorized personnel access sensitive information are just a few practices that improve your data protection strategies. This protects patient information from cyber threats and secures your reputation as a trusted healthcare provider. Less risk of data breaches helps assure patients that their private information remains private.
Fostering trust and patient loyalty
When patients know their sensitive health information is handled securely, their confidence in your services grows. This trust translates directly into patient loyalty. Being a HIPAA-compliant organization can also be a strong marketing point and attract patients who prioritize privacy and security.
Competitive edge in the healthcare industry
Patients today are more informed and concerned about digital privacy than ever before. Demonstrating that you prioritize their security can be a deciding factor for patients when choosing a healthcare provider. It also streamlines partnerships with other entities that prefer or require compliance as a prerequisite for doing business.
Streamlined operations and efficient data handling
Establishing clear data management protocols, training staff on consistent procedures, and utilizing secure and compliant technologies leads to more structured workflows. This results in fewer errors simplified information tracking, and quicker responses to data requests, improving operational efficiency. These improvements can lead to better patient service and reduce operating costs.
How to Achieve HIPAA Compliance
Achieving HIPAA compliance involves a series of steps.
- Conduct a thorough risk analysis to identify potential vulnerabilities to electronic PHI's confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Develop and implement policies and procedures to mitigate these risks and ensure they align with the HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules.
- Make sure that all employees understand the importance of HIPAA compliance and their role in maintaining it. Regularly review policies and procedures, making updates as necessary. This includes changes in technology or operations that might affect the security of PHI.
- Work with your IT department or an external tech provider to ensure that all electronic systems used to handle PHI are secure. This includes implementing encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates.
- Promote good data security practices and clarify that safeguarding patient information is everyone's responsibility to establish a culture of compliance within your organization.
HIPAA Compliance Audit
A HIPAA compliance audit is a formal review of how a Covered Entity or Business Associate is adhering to the HIPAA regulations. As part of the audit process, organizations must demonstrate the proper safeguards to protect patient privacy and secure PHI.
Regular internal audits can prepare you for an official Office for Civil Rights (OCR) audit. To pass an audit, you must adhere to the Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rule and have documentation to back up your compliance efforts. Consider conducting mock audits to practice your response to an OCR audit.
You should also stay informed about the latest updates to the audit protocols released by HHS. Keep detailed records of all your HIPAA compliance activities, which will be crucial if you are selected for an audit. The primary goal is to pass the audit and ensure continuous patient information protection.
Become HIPAA-Compliant with Kohezion
Kohezion offers a sophisticated online database software solution to securely organize, track, and store sensitive patient data, helping organizations become HIPAA compliant. Kohezion offers robust data encryption, fine-tuned access controls, and comprehensive audit trails to ensure your data management processes align with HIPAA standards.
Conclusion
Achieving HIPAA compliance offers many benefits beyond following the law. This includes building trust with patients and helping streamline your operations. Staying compliant is an ongoing effort. You need to keep up with regulation changes, provide thorough training, and put the right security measures in place.
Prioritizing patient data security protects against breaches and legal issues while also strengthening your reputation as a reliable healthcare provider. Use this checklist to make sure your practice is ready for whatever comes its way in 2024 and beyond.
Start building with a free account
Frequently Asked Questions
HIPAA training should be conducted for all new hires to ensure they understand their obligations regarding PHI from the start. Ongoing training should also be provided annually or more often if there are significant changes to HIPAA regulations or your organization’s policies. Regular training updates help maintain a culture of compliance and keep staff members aware of their responsibilities.
Penalties for non-compliance with HIPAA can be severe, ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum of $1.5 million per year for identical provisions. The fines can be even higher in cases of willful neglect, and criminal charges may be filed.
Both covered entities and business associates must comply with the HIPAA privacy and security rules, but the specifics can differ. Covered Entities are the direct handlers of PHI and face a wider scope of regulations regarding the use and disclosure of PHI.
Business Associates are primarily concerned with protecting the PHI that they access, use, or disclose on behalf of a Covered Entity, as outlined in their Business Associate Agreement. Both must ensure their practices meet HIPAA requirements.
Organizations should regularly check the HHS Office for Civil Rights website, subscribe to newsletters from trusted HIPAA-related resources, attend industry conferences, and participate in relevant training programs to stay informed about HIPAA regulation updates.
The HIPAA Enforcement Rule outlines how investigations, compliance reviews, and proceedings for HIPAA violations are conducted. It includes the tiered civil penalty structure based on the level of perceived negligence and sets a maximum penalty amount. The Enforcement Rule also describes the process for imposing these penalties and the parties' rights, such as hearings and the right to appeal.


