What is Automated Decision Making?
Automated decision-making is when decisions are made through automated means without the need for human involvement. This approach can make operations in businesses like yours faster and more efficient. This lets you focus more on human-centric tasks while minimizing errors and bias in decisions.
How Does Automated Decision-Making Work?
Automated decision-making, in simple terms, is like your business operating on autopilot. It's about using technology to make decisions without human intervention.
For example, think about buying an air ticket. When you go online to book, the ticket price fluctuates based on seat availability and when you make the purchase. This is automated decision-making in action.
The automated decision-making process begins with the collection of various data points, including information such as seat availability and the time of purchase. Once gathered, this data undergoes processing where it is analyzed and evaluated against predetermined rules and parameters. Finally, based on this processing, the system arrives at a decision, determining the final price for the product or service in question.
Benefits of Automated Decision-Making
Increased efficiency and productivity
Decision Automation (DA) is your new ally to boost productivity and cut down on risk and errors. It's not about robots taking over; it's about making your decisions smarter, faster, and consistent.
- DA ramps up your productivity. It reacts in real time, reducing the gap between an event and an action. All that saved time adds up to increased efficiency.
- With DA, you're making decisions grounded in data. The World Economic Forum noted that 43% of businesses may reduce their workforce due to technological advances, while 34% intend to bolster their workforce to aid technology integration.
- DA minimizes risks. DA leverages data, models, algorithms, and expertise to make its decisions, cutting down the possibility of human error.
- DA ensures compliance. It reduces regulatory or contractual errors, saving you from potential non-compliance fines.
Increased accuracy of decisions
Automated decision-making (DA) can drastically bolster the accuracy of your business's decisions. Here's why:
- DA is data-driven: It's contingent on data and calculations, unlike discretionary decisions. The more data, the more precision, offering you insights that are data-backed and not on guesswork.
- Provides real-time awareness: DA swiftly reacts to real-time data. This gives you a complete and updated picture of situations as they occur, confirming that your decisions are always relevant.
- Minimized risks and errors: With DA, the likelihood of human errors in decisions is significantly reduced. Error-free decisions mean happier customers and reduced compliance concerns.
- Allows continuous learning: DA software learns from past outcomes, success or failure, and updates its algorithms and rules to improve future decisions.
Improved consistency of decisions
Here's how automated decision-making can heighten consistency in your organizational decisions:
- It works tirelessly, ensuring standard, error-free decisions round the clock, eliminating human element inconsistencies.
- This method fosters transparency, as it provides a clear model of how every decision is made.
- It enhances compliance, helping you avoid regulatory mistakes and potential fines.
Increased flexibility
Automated decision-making makes fast, error-free decisions around the clock and amps up flexibility within your organization. Here's how:
- The system offers consistency across all decisions, something individuals or teams may struggle to achieve.
- Decision modeling becomes streamlined and transparent.
- It enhances compliance, cutting down regulatory or contractual errors.
Reduction of human error
Automated decision-making substitutes emotional judgment with rational data-driven choices and significantly reduces human error.
- Decision Automation leverages data, makes accurate predictions, and can help you act promptly, reducing the time and risk of manual decision-making.
- It embraces consistency, ensuring that decisions across your company are not biased or inconsistent.
- The automated system learns from past decisions, thus updating processes to avoid errors.
- It provides the chance for domain experts to intervene when full automation hits a roadblock, bringing human insight back into the picture.
- This system enhances compliance, shielding you from regulatory breaches and consequential fines.
Increased speed of decision-making
Automated decision-making takes your gathered data, and applies decision logic, models, and algorithms. and makes efficient decisions.
Ability to handle large amounts of data
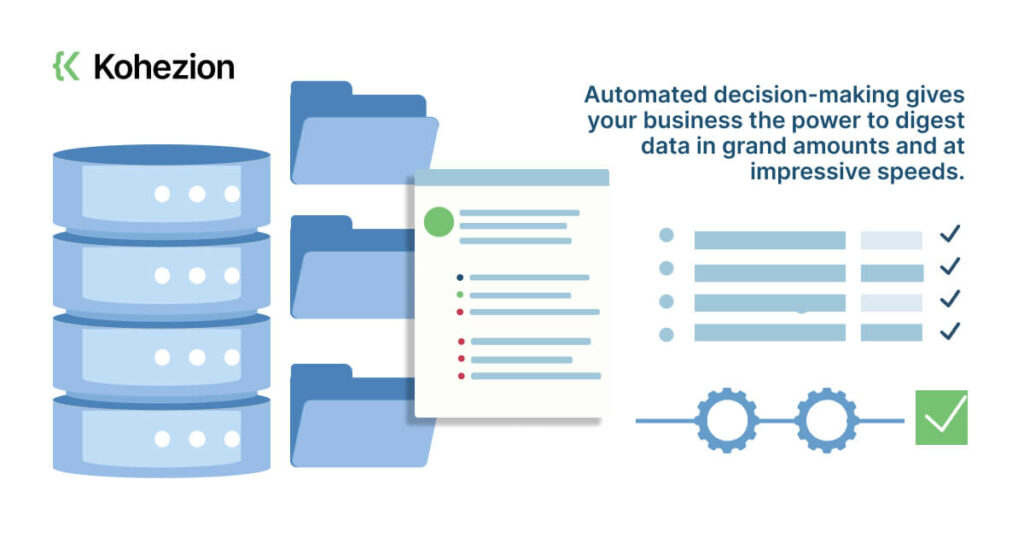
This prowess can revolutionize your decision-making process significantly.
- Automated decision-making gives your business the power to digest data in grand amounts and at impressive speeds.
- This system sifts through and classifies information with precision, turning data into insights.
- For instance, in marketing, this tech uses data to pinpoint who to target, when, and how, fostering campaigns that resonate and convert.
- Therefore, automated decision-making doesn't just handle data; it harnesses it, enabling you to tap into insights that wouldn't be possible otherwise.
Increased accuracy of predictive analytics
Automated decision-making uses real-time data to make informed choices and enhances the precision of predictive analytics.
It uses vast amounts of current data, abolishing the risk of decisions based on dated information or individual bias. For example, in finance, robo-advisors can examine diverse trading data and prompt the next ideal investment moves. This automation leads to:
- Quicker, data-driven responses
- Minimized risks of mistakes and prejudice
- Real-time, relevant decisions
Increased ability to identify patterns
The rise of automated decision-making technology has brought about an impressive capacity for pattern identification. This means that these digital technologies can sift through enormous amounts of data rapidly and pinpoint patterns and trends that the human eye might miss.
For example, automated decision systems are being used in job applications. The system can scan hundreds of CVs at once, determining whether candidates fit certain patterns or criteria set by employers. The efficiency of this system tackles time-consuming tasks, enabling quicker decisions while eliminating human error, thus ensuring more consistency.
Increased transparency and accountability
Automated decision-making (ADM) makes decision-making processes clear and trackable and can heighten your organization's transparency and accountability. ADM imparts trust and assurance within and beyond the organization. Here's how:
- It allows open access to algorithms, reinforcing transparency and enabling audits.
- It offers clear explanations of decision-making processes, fostering understanding and trust.
- It promotes the use of simple models, ensuring interpretability and reducing bias.
- It mandates transparency measures, including plain language descriptions and results of audits.
- It obliges risk assessments along with proactive disclosures about how and where algorithms are being used.
Challenges and Solutions in Automated Decision Making.
Unclear logic behind automated decisions
Automated decision systems might seem like a boon, making robust decisions swiftly and efficiently. However, the problem arises when these complex mechanisms, particularly ones like neural networks, can't clearly explain their reasoning.
Imagine being denied healthcare, or a job, yet the reasoning behind the decision is obscure at best. You're left in the dark, unable to contest because the computer says 'no'. This exact scenario played out when an algorithm unexplainedly reduced medical care for patients, impacting health and well-being.
The solution? Federal institutions need to ensure their automated systems can provide understandable explanations for their decisions. This transparency helps prevent consequences from unexplained decisions, safeguarding public trust and individual rights.
Lack of transparency
The lack of transparency spikes problems particularly when algorithms go wrong, like when an algorithm unduly reduces a patient’s medical care.
The solution to this challenge comes in two-fold:
- Implement regulatory measures for transparency: The Directive mandates federal institutions to dish out clear explanations of how and why a decision is arrived at by automated systems. Plus, it needs source code to be open when possible, boosting the ability to examine and critique a decision.
- Use simple models: This ensures the decision-making process is not only explainable but also interpretable, making it easier for you to understand the reasoning behind a decision.
Inability to explain the decision
The challenge of 'Inability to explain the decision' in automated systems can be problematic, especially when systems are complex and not easily elusive. Specifically, issues arise when individuals or companies can't understand how a system arrived at its output.
Solutions to this challenge include:
- Picking the right model for human interaction for each decision ensures decisions can be questioned and understood.
- Monitoring each micro-decision-making system, regardless of the level of human interaction, to ensure efficient and transparent decision-making.
- Capturing at least two metrics that focus on this aspect to measure decision-making effectiveness.
- Documenting how the system made the decision, not just the final decision, enables a better explanation of "bad" decisions.
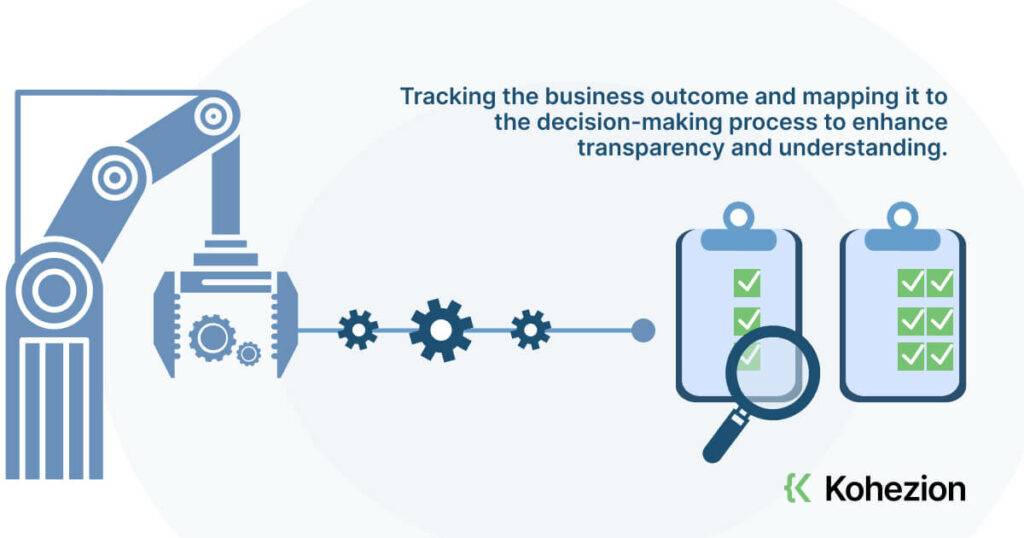
- Tracking the business outcome and mapping it to the decision-making process to enhance transparency and understanding.
Inequality of treatment
Automated decision-making can unintentionally exacerbate inequalities due to biases within the data. For example, algorithms based on biased historical data may amplify past inequalities in race, class, and gender.
Also, a lack of diverse representation within the data can compromise accuracy. Examples include facial recognition systems working less effectively for different skin colors or gender, and recruitment models favoring certain genders.
Potential solutions include:
- Performing impact assessments of algorithms
- Implementing quality assurance measures for the data and algorithms
- Ensuring proactive transparency about the use of algorithms
- Promoting ongoing oversight and review with independent and community input
- Incorporating a politics of care to acknowledge and respond to complexities and potential impacts before implementation.
Lack of accountability
Lack of accountability in automated decision-making can pose real challenges. Ponder this - an automated system makes a decision that involves you, but no one can explain the decision's logic.
So, how can we counter this problem?
- There is a need for robust accountability in adopting Automated Decision Systems (ADS).
- Proofs of accuracy, effectiveness, and safety are crucial.
- Legal reviews ensure your data is handled responsibly.
- Government agencies should thoroughly scrutinize their ADS procurement.
Lack of human oversight
Unconsciously, you may have been affected by automated decision-making. It's how governments decide on your medical care or police patrol routes. But there's a snag - many times these systems lack essential human oversight, leading to unexplained outcomes.
The solution: Let experts audit your programs to mediate bias, and put humans in charge of final decisions especially when they influence well-being.
Inability to adjust to changing circumstances
Facing adjustments in automated decision-making systems can be hard. Sometimes, the system may unpredictably alter decisions such as reducing medical care, which can be harmful. The issue here is the 'why' - why did this change occur in the first place? The solution is understanding the system's logic to ensure there's transparency.
So, the workaround includes:
- Reviewing the system and pinpointing irregularities.
- Adjusting your system to make its decision-making process understandable.
- Always be ready to analyze and iterate for improvements.
Unreliability of the decision-making algorithms
Facing an automated decision-making system can be a double-edged sword. It's efficient and nifty but its unreliability can leave you straining.
- Data-driven algorithms often become complex, making the reasons behind decisions obscure.
- Their performance is inconsistent; they can work flawlessly or nosedive without warning.
- An overly automatic system can spin off in unexpected directions due to the absence of human involvement.
To handle these challenges:
- Select an optimal human engagement model for the decision at hand.
- Ensure every micro-decision process is constantly monitored.
- Maintain records of metrics that measure decision-making effectiveness.
Potential for unfair treatment of data
Data in automated decision-making can sometimes be handled unfairly, leading to biased outcomes. Be aware of several risks:
- Profiling could happen without your knowledge.
- Your personal data may be used unexpectedly.
- It can be hard to comprehend the decision-making process.
- Decisions made could negatively affect certain individuals.
- Correlation findings may not always be significant.
- Automated systems could potentially discriminate based on race, class, or gender.
- If data is flawed or incomplete, the results could be compromised.
- The predictive ability of systems might be unexplainable.
Risk of infringing on privacy rights
The use of automated decision-making (ADM) can unintentionally infringe on your privacy rights. This 'black box' system, often hard to analyze, can lead to a lack of transparency about how your data is utilized.
- Your confidential data is used without your awareness or understanding, causing discomfort or even harm.
- For an organization, this infringement can lead to loss of trust, reputational damage, and potentially legal issues under laws like the GDPR.
What software can help automated decision-making in an enterprise?
1. Decision Automation Systems
Decision automation systems can help with:
- Speedy data processing
- Scalable, consistent decisions
- Leveraging AI and contextual data
- Minimize human errors
However, you might want to consider the other side of the coin.
- Cost: Depending upon complexity, DAS can be expensive.
- Ambiguities: In situations needing subjective judgment, DAS might falter.
- Transition Phase: Implementing DAS might disrupt existing processes.
- Overdependence: Over-reliance on DAS leads to manual decision-making skills decline.
- Maintenance: Regular system updates and adaptations can be a challenge.
Pricing of a DAS depends on the required features, complexity, and scalability.
2. Data Management Platforms
Data Management Platforms (DMPs) make use of advanced AI tech for automated decision-making, making the whole process less cumbersome.
- Automates data analysis for quick decisions
- Enhances campaign targeting based on precise user data
- Uses large-scale, diverse datasets
On the pricing note, DMPs often require significant investments due to the cost of technology and data storage.
3. Analytics Tools
Analytic tools are a viable alternative, making business decision-making more efficient and effective.
Features offered:
- Robust data analysis
- Automated decision-making capabilities
- AI-tech backing for smarter marketing strategies
Pros:
- Speeds up data analysis and saves time
- Machine precision provides greater accuracy
- Identifies precise targets and enhances marketing efforts
- Utilizes data to make informed decisions
- Reduces human error
Cons:
- High initial costs for implementing the tools
- Need for staff training in using the tools
- Risk of over-reliance on automation
- Potential loss of data or information breaches
- Difficulty in analyzing qualitative data
When it comes to pricing, these tools can be expensive initially, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs.
4. Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) offers a dynamic way to automate business decisions, given its capacity to learn, analyze, and solve complex problems from large data sets.
Here are its prime features:
- Uses pattern matching through deep neural networks
- Adaptable to new challenges
- Can be applied across different sectors
Pros:
- Improves consistency and quality
- Speeds up decision-making
- Reduces risk of errors
- Flexible and adaptable
- Cost-effective
Cons:
- Requires significant data input
- Potential for algorithmic bias
- High computational power intense
- Prone to cyber-attack
- Complex implementation.
5. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics using AI technologies significantly empowers your enterprise decision-making and automates the process for improved efficiency and reliable results.
Top features:
- Analyze vast sets of data
- Pinpoint trends and patterns
- Enhance decision-making
- Streamline operations
- Boost profit margins.
Pros:
- With ample data, predictive analytics is more accurate.
- AI automates routine decisions saving valuable time.
- Provides data-driven insights and enhances profit.
- Tailors financial services to individual needs.
- Reduces risk through informed decisions.
Cons:
- Data-driven analytics can perpetuate past biases.
- Unreliable if data is disproportionate or inaccurate.
- Training AI models on skewed data can amplify inequalities.
- Certain systems like facial recognition may work inequalities.
- Mistakes can be costly and detrimental to business.
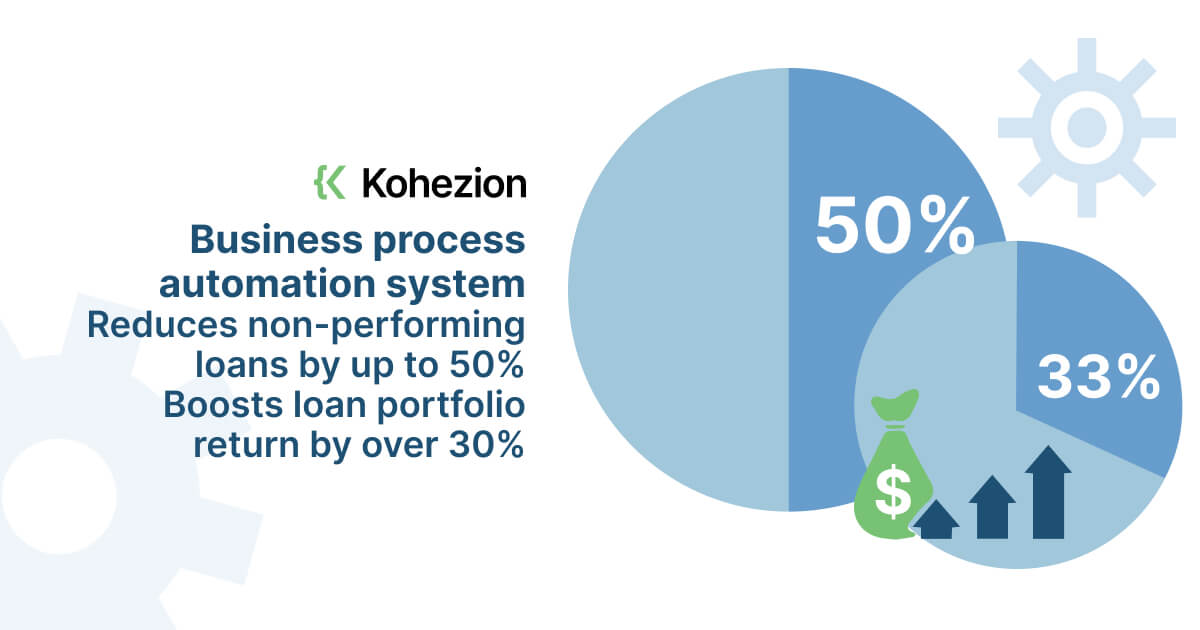
6. Business process automation system
Business process automation is an efficient alternative to traditional decision-making strategies. It reduces the valuable time you spend on tedious, repetitive tasks - opting for accurate, fact-based results instead.
Main features include:
- Makes fast and error-free decisions
- Improves consistency and compliance
- Employs AI technology like GiniMachine for superior results
Pros:
- Reduces non-performing loans by up to 50%
- Boosts loan portfolio return by over 30%
- Evaluates an astonishing amount of data quickly and enhances efficiency
- Makes you capable of working around the clock
- Saves time for more human-facing tasks
Cons:
- Depends on clean and well-flowing data
- Requires fine-tuning to improve efficiency and accuracy
- Involves a learning process
- Can be dependent on the quality of the algorithms
- May sometimes overlook nuanced human judgment.
Conclusion
The adoption of automated decision-making stands as a watershed moment for businesses, promising unparalleled efficiency and precision while demanding vigilant attention to ethical, transparent, and accountable implementation. Its integration isn't merely a technological upgrade; it represents a strategic shift that, when harnessed prudently, can redefine how organizations operate and innovate.
The spectrum of tools available to facilitate automated decision-making is vast, from decision automation systems to machine learning and predictive analytics. Each tool bears its strengths and limitations, posing considerations of cost, complexity, and reliance on human intervention.