To create an effective enterprise data strategy, we need to understand the importance of aligning data with business goals, prioritize data security and governance, utilize advanced analytics, involve stakeholders, and continuously adapt the strategy to evolving data needs and technologies.
Let's dive in.
What is enterprise data strategy?
An enterprise data strategy can be defined as a comprehensive plan that outlines how an organization will collect, organize, process, and utilize its data based on business priorities, size, and industry trends. Why is important for businesses to have a data strategy? That's because it helps them turn the volumes of data pouring into their business ecosystem into real profit.
What is a good enterprise data strategy? It is a strategy that is not only practical and relevant but also evolutionary, and connected/integrated. It should include key elements such as data ingestion and storage, the use of datasets, master data management, reliable retrieval and reporting, and incorporation of unstructured data. An effective enterprise data strategy can assist businesses in achieving their objectives by improving data quality, integrity, and accessibility.
What are the key components of enterprise data strategy?
As a comprehensive plan, data strategy consists of a plethora of elements. Some are essential, while others can be skipped. Listed below are 10 key components of every enterprise data strategy:
- Business Objectives
- Data Sources
- Data Quality Standards
- Data Maturity Level
- Data Strategy Team
- Data Architecture
- Data Governance Systems
- Business Needs
- Data Priorities
- Information Architecture
What are the benefits of having an enterprise data strategy?
The benefits of having an enterprise data strategy are numerous. They include everything from discovering data's value to the organization and identifying strategic priorities for data management to detecting current data management challenges. Keep reading to discover the main benefits of developing an enterprise data strategy.
1. Better Understanding of Data
Richer understanding of data provides a roadmap for getting data into a form that business teams can use. With an enterprise data strategy, organizations can find the relevant data sources required by analytics teams.
2. Increased Business Value
Yes, this is possible by enabling organizations to make more informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and identify new revenue streams. A data strategy allows businesses to harness the power of their data to gain unique insights. For instance, by leveraging customer data, organizations can personalize their marketing efforts, improve customer service, and increase customer engagement.
3. Improved Data Quality
Let's say a customer gender identifier service classifies the wrong gender for a customer. This could lead to incorrect gender-based recommendations, resulting in the loss of that customer. Data quality checks enable companies to avoid massive losses due to incorrect data, maintain customer trust, and improve competitiveness.
4. Enhanced Efficiency & Effectiveness
Better efficiency and effectiveness allows companies to streamline their operations and improve business outcomes. For instance, identifying relevant data sources before implementing data integration processes can reduce the cost of managing data and increase data analysts' confidence in the accuracy of the data.
Organizations can leverage their data to make informed decisions, streamline operations, and identify areas for improvement. From back-office processes (like payroll and accounting) to central business operations, having a data strategy ensures that data management is improved across the entire company.

5. Increased Ability to Analyze and Interpret Data
This can be done in several ways, including:
- Improved Data Governance
- Better Data Management
- Real-time Insights
- Increased Analytics Potential
When combined together in a data strategy, these allow organizations to handle the challenges of multi-cloud environments, a proliferation of data, as well as the need to manage and govern all this data. Ultimately, this can help organizations to achieve their goals and meet the demands of their customers.
6. Increased Ability to Predict Outcomes
Prediction of outcomes is key to success. By analyzing data, companies can identify trends, as well as customer behavior and preferences, which can be used to make predictions about future outcomes. And accurate predictions can also help companies optimize their operations and improve profitability.
7. Complying with Regulations
While not so apparent, the increased ability to comply with regulations makes it easier to identify and prioritize regulatory requirements while establishing clear policies no matter the industry. Let's check two examples.
- In the healthcare industry, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires companies to protect the privacy of patients' health information. A data strategy can help ensure compliance with HIPAA by providing guidelines for data governance, security, management, and computing.
- In the financial industry, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) requires companies to maintain accurate financial records. This is where an enterprise data strategy comes in! It can help ensure compliance with SOX by providing guidelines for data quality, data lineage, and data mastering.
8. Improved Security and Protection of Data
With a well-defined data strategy, companies can better protect their data while minimizing the risk of data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other security incidents. It's best to combine it with regular data backups and security audits. Even so, you should have a disaster recovery plan, just in case.
Steps to create an enterprise data strategy
Step 1: Identify key stakeholders
Here are some examples of primary stakeholders:
- internal IT teams
- business units
- data consumers
- project management
- executive sponsorship, and finance
Bring stakeholders along in the process and identify key decision-makers to increase your chances of success. So, how can you identify these stakeholders? Check their role in the organization, their level of influence, and their interest in the data platform.
Step 2: Identify company goals and objectives
Next, start asking questions such as:
- Where the data will live?
- What type of data will be collected?
- How the data will be organized?
Make sure your business objectives align with the overall business strategy. Ideally, this review process should be done on a quarterly or monthly basis to ensure that the data strategy stays up to date. Take a clear approach to identifying these goals and involving stakeholders to come up with a comprehensive plan on how to manage the data of your company/organization.
Step 3: Outline your data architecture
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to outline data architecture:
- Provide a current state technical architecture landscape.
- Perform an inventory of data resources such as databases and content management.
- Develop a strategy that includes the scope, ETL/ELT approach, querying, analytics, standards, security, etc.
- Create a future state architecture map as part of the deployment scope.
- Map your data infrastructure, architecture, and tools to ensure nothing slips through the cracks of governance.
- Create data catalogs to help users find the data sets they need and store all your data in a single platform.
- Draft an initial architecture of the solution based on information gathered in the discovery phase.
- Sequence the strategic initiatives and review how each deployment can support your data vision.
Step 4: Assess the technology options
There's a broad range of different solutions available to support data management, including:
- Warehousing - It involves storing structured data in a centralized location for easy access and analysis.
- Data lakes - They are meant to store both structured and unstructured data in a raw format.
- Cloud-based solutions - These solutions can easily be scaled up or down based on business needs.
- Data governance tools - The goal of these tools is to help ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
Each option comes with its own set of limitations. For example, there are scalability challenges with data warehousing and security concerns with data lakes. Likewise, there are potential vendor lock-ins with cloud-based solutions.
Step 5: Conduct a strategy session to identify the best approach for your company
Here are some questions that should be addressed during the session include:
- What are the organization's data needs?
- What data is essential for decision-making?
- What data is currently being collected, and how is it being used?
- What are the data management processes that need improvement?
Step 6: Define organizational structure and responsibilities
Typically, a cross-functional team led by a data or IT leader should be established, with clear ownership assigned for each part of the data pipeline. The person leading the team has a deep understanding of the data platform architecture. The teams who produce the data should also have some level of ownership and accountability for the data.
Step 7: Implement the data platform architecture
At this stage, we consider key components such as data storage, processing, and management. Common data platform architectures include data warehousing, data lakes, and cloud-based solutions. These architectures can be customized to suit the specific needs of your enterprise, such as incorporating data governance and data quality assessment.
Systems that can help with the implementation of enterprise data strategy
1. Data Quality Management System
This system comprises a data profiling approach, active/passive quality checks, a DQT rule book, and a DQ application. Moreover, the system also identifies data quality metrics reporting per load cycle and post-go-live while outlining data cleansing reporting and approach at the same time. Take advantage of it to maintain high data quality standards and enhance customer satisfaction.
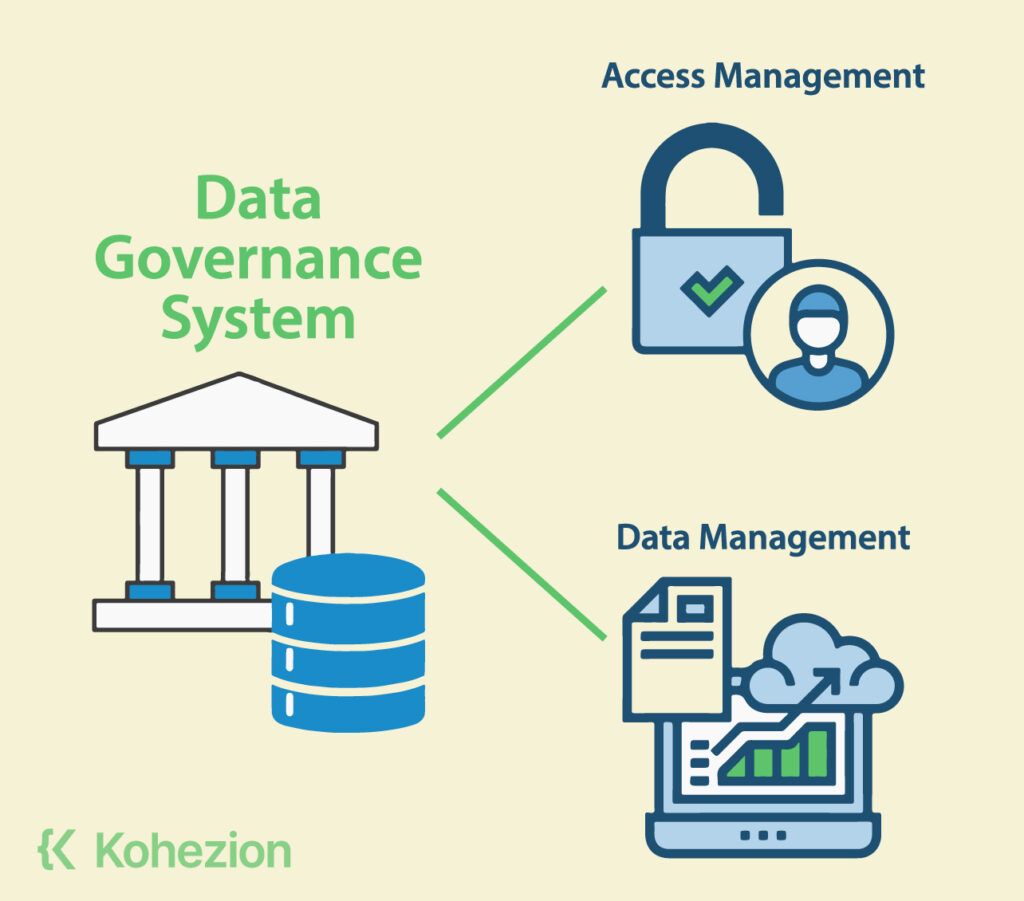
2. Data Governance System
Basically, a Data Governance System is meant to help define who can access and modify data while establishing processes, policies, and standards for effective data management. Its key features include:
- authentication and authorization
- information architecture
- data provisioning
- rights management
- data catalog and classification
- data lineage, and
- data mastering
Keep in mind that over-engineering the system can slow down progress and limit business value. Successful implementation of a Data Governance System requires balancing the need for governance with the need for agility and innovation. Some examples of industries or organizations that have successfully implemented it include healthcare, finance, and government agencies. Just about any industry and enterprise can implement it. The key is to do it properly to achieve success.
3. Data Integration Process
Data integration is the process of combining data from different sources into a single, unified view. Before implementing a data integration process, be sure to identify relevant data sources required by your analytics team. A hybrid data management approach allows for the management and serving of real-time and batch data. It enables near-real-time insights for the business team. Give it a try!
4. Business Intelligence Systems
BI tools and technologies enable enterprises to collect, analyze, and present data in a meaningful way. What's more, BI systems can assist in the implementation of an enterprise data strategy by providing a centralized platform for data management and analysis.
This is a good reason to start leveraging BI systems. Apart from gaining data insights and identifying trends, it will allow you to make informed decisions based on real-time information. In addition, BI systems can help you streamline data processes across different departments, allowing your company to improve overall productivity.
5. Big Data Platforms
Some popular big data platforms include Amazon EMR, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, just to name a few. These platforms provide businesses with a variety of tools to manage and analyze large amounts of data.
6. Query Engines
The main goal of every query engine is to make it easier for users to query multiple data sources using a single query. How does it work? The engine's architecture is designed to cut through the clutter of analytical data and provide business insights. There are different types of query engines available, including reporting dashboards, advanced analytics or decision systems, as well as ad hoc/data discovery systems.
7. Information Architecture Systems
Chances are you have used some types of information architecture systems. If not, start using them as soon as possible because they are essential for implementing an effective enterprise data strategy. These systems include data analytics, modeling, visualization, transformation, and enrichment. Some commonly used information architecture systems include marketing dashboards, customer relationship management systems, and supply chain management systems.
8. Data Science Tools
Data science tools aid in the implementation of an enterprise data strategy. For example, popular data science tools such as Dataiku and Tableau can be used to analyze data from different sources.
9. Information Collection Systems
These systems are responsible for collecting, storing, and analyzing data from various sources. They use data analytics, modeling, visualization, transformation, and enrichment to convert raw data into useful information that can be applied strategically. While there's a wide range of information collection systems, some common examples include databases, file systems, and marketing dashboards.
10. Data Analytics Platforms
There is a huge selection of data analytics platforms to choose from, including popular ones like AWS, Azure, Dataiku, Snowflake, and Tableau. You want to select and use platforms with a well-defined workflow. They also need to allow for the collection and management of different data sources. These platforms should be selected based on specific use cases and factors shared by the analytics teams.
ERP vs Low code database system for enterprise data strategy implementation
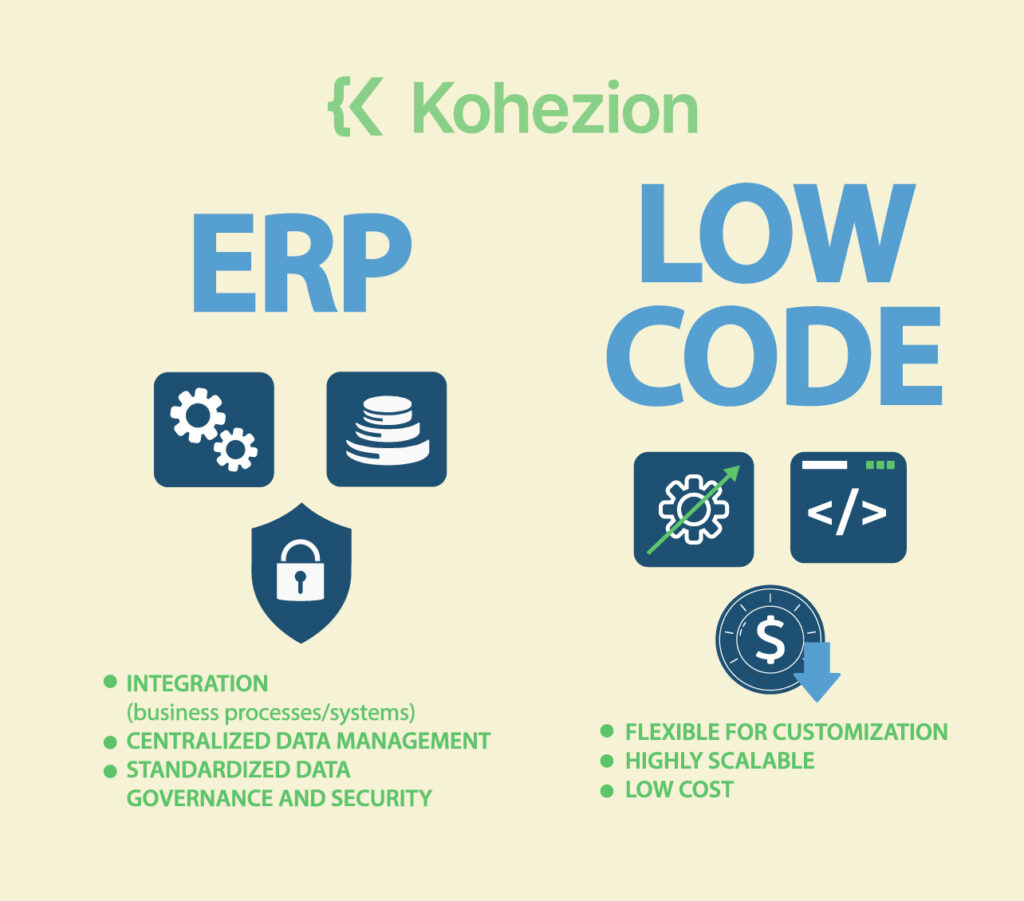
Are you interested in implementing a data strategy? As an enterprise, you essentially have two options: incorporating it into an ERP system or using a low-code database system. Let's check their advantages and drawbacks.
|
ERP System
|
Low Code Database System
|
||
|
PROS |
CONS |
PROS |
CONS |
|
Integration with existing business processes and systems |
Limited scalability |
Low cost and easy to implement |
Limited integration with existing business processes and systems |
|
Centralized data management |
High cost and complexity |
Highly scalable |
Limited data governance and security |
|
Standardized data governance and security |
Limited flexibility for customization |
Flexible for customization |
Limited standardization |
ERP systems are suitable for industries such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare, where large amounts of data need to be managed and analyzed. Low-code database systems are more suitable for industries with a need for scalability and flexibility for customization such as finance, insurance, real estate, e-commerce, and social media.
Data governance
With regard to data governance, ERP systems are typically more rigid and have built-in data governance features, whereas low code database systems require a more manual setup of data governance policies. What makes ERP systems popular is that they have pre-built access controls and data quality management features. One of the best things about low-code database systems in this regard is that they offer more flexibility in terms of customization, so you can tailor them to specific business needs.
Data architecture
The data architecture of an ERP system is typically highly structured and centralized, with a single source of truth for all data. This makes it highly suitable for standardizing enterprise data and ensuring data consistency and accuracy. As for low-code database systems, they feature decentralized data architecture with multiple versions of the truth. This makes these systems ideal for customizing data to support specific business needs and enabling agile development.
Data access
An ERP system and a low-code database system have different data access capabilities, which is another thing you need to consider when implementing an enterprise data strategy. A typical ERP system offers a wide range of features and functionalities, including data access, reporting, and analytics. Conversely, low-code database systems provide simplified access to structured and stored data, allowing users to interact and manipulate data without extensive programming knowledge.
Data quality
Comparing an ERP system to a low-code database system, the former is usually more reliable in terms of data quality. ERP systems are designed to handle complex business processes and data, ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data. Low-code database systems may have limited data quality controls and may not have the same level of integration and standardization as ERP systems. If data quality is your top concern, consider this fact when implementing an enterprise data strategy.
Data transformation
In scenarios where an enterprise has complex business processes that require integration across multiple functions, an ERP system is typically (but not always) more suitable. On the contrary, a smaller company with simpler business processes may benefit more from a low-code database system that allows for more customization and agility.
Data insights
Probably one of the main advantages of using an ERP system for implementing a data strategy is that it provides a comprehensive view of the business operations. Thus, it allows for better control and management of data across different departments. In contrast, a low-code database system allows for faster development and deployment of applications and databases, but may not provide the same level of integration and control as an ERP system.
Data control
In terms of data control, ERP systems are the winner. That's because these systems provide a higher level of data control through standardized processes, strict data governance, and built-in security features, ensuring data integrity and regulatory compliance. Even so, low-code database systems offer more user-driven data control by allowing users to define and customize data models, access permissions, and validation rules according to their specific requirements.
Type of companies that will benefit from enterprise data strategy.
1. Large companies
Large companies, in particular, benefit from implementing enterprise data strategy. There are many examples. For instance, Walmart implemented an enterprise data strategy that allowed them to analyze customer data and optimize their supply chain, resulting in significant cost savings. Another good example is General Electric, which implemented a data strategy to monitor the performance of its aircraft engines and predict maintenance needs, leading to reduced downtime.
2. Complex organizations
Implementing a data strategy can considerably benefit (in multiple ways) complex organizations, too. By having a clear and well-planned data strategy, these organizations can better leverage their data to enable efficient reporting and decision-making systems. This, in turn, can impact their business outcome capabilities and lead to a competitive advantage. Industries and sectors that can benefit from an enterprise data strategy include finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, among others.
3. Enterprises with multiple departments
Enterprises with multiple departments should also consider implementing an enterprise data strategy to reap benefits by having a centralized approach to data management. This can result in potential cost savings and efficiency gains. A centralized data function with a single CDO can ensure consistency, while decentralized data management with unit CDOs can prevent data silos. Companies like Wells Fargo, CIBC, and P&G have successfully implemented CDOs responsible for both analytics and data management.
4. Enterprises that rely on data-driven decision making
If your company or organization relies heavily on data-driven decision-making, implementing an enterprise data strategy would bring you a lot of benefits to your business. How? It can make sure that the data is of high quality, reliable, and properly governed. This allows for making informed decisions based on accurate data, regardless of the industry. For example, a retail company can use data to optimize its inventory management, while a healthcare organization can use data and artificial intelligence to improve patient outcomes.
5. Enterprises that need to scale their data resources
Enterprises that generate large amounts of data - especially those in the healthcare, finance, and retail sectors - can make use of implementing an enterprise data strategy to scale their data resources. Further, companies that operate in a complex data environment, such as those with multi-cloud environments or a proliferation of data sources, can also derive benefits from a clear data strategy. A solid enterprise data strategy will enable these companies to derive value from their data.
6. Enterprises with changing data needs
In this case, a data strategy must evolve over time in order to keep pace with new technologies, customers, markets, regulations, and a virtually endless number of other priorities. It is recommended that these enterprises identify their changing needs and reassess their data strategy every 6 months to a year so as to stay ahead of the curve. They are advised to make necessary adjustments to their strategy whenever needed.
7. Enterprises that want to optimize their data storage strategy
This refers to companies that deal with a huge volume of data from diverse sources, including social media, IoT, and multimedia content. Such companies need to ensure that their data is stored and processed efficiently at edge locations and in the cloud as well. They can benefit from improved data quality, integrity, and accessibility, which eventually leads to better business decisions and increased profitability.
8. Enterprises that want to improve the quality of their data
In fact, every enterprise wants to improve the quality of its data. If this is one of your top priorities, it's high time to develop an enterprise data strategy. You want to have a data strategy that ensures that every piece of data is accurate, relevant, and reliable. For instance, data quality requirements should be established, and key performance indicators (KPIs) should be defined to determine the quality of data and what actions need to be taken if data quality requirements are not met.
9. Enterprises that want to improve their data analytics capabilities
Another good reason for implementing an enterprise data strategy is to improve data analytics capabilities. Why is it important for companies to prioritize their investment strategy and harness their data? Simply because it allows them to gain a competitive advantage and avoid being left behind in today's data-driven business environment.
10. Enterprises that want to move from a unifying data strategy to a data product approach
What does the shift to a data product approach mean? Fundamentally, it means that data is viewed as a fully functional business area, developed, marketed, quality controlled, enhanced, and with a clearly tracked value. Many successful companies have made this transition. HubSpot, for example, has implemented a data strategy focused on delivering data bit by bit and incorporating it into existing strategic initiatives.
Ways that an enterprise data strategy enables big data analytics
1. A Unified Data Source
By offering a consolidated repository for all pertinent data sources, a unified data source can significantly improve big data analytics. This facilitates data access for the analytics team, minimizes effort duplication, and enhances data management throughout the entire organization. With the use of machine learning to mine the data, prediction, and recommendation, systems can be trained to identify customer data from disparate sources and provide a personalized user experience and a 360-degree view of the customer.
2. Data Strategy Team
Having a dedicated data strategy team is critical when creating an enterprise data strategy. The team is supposed to be cross-functional and include members from both business and technical functions. The team's objective is to drive data activities across functions and groups, with a holistic view across domains. The data strategy deployment orchestrator should lead the team and have a strong grasp of the overall data strategy deployment roadmap and playbook.
3. Data Maturity Level
The Data Maturity Level can be regarded as a framework that helps enterprises understand how data-driven they are and what they need to do to improve their data strategy. There are four stages of data maturity:
- Data aware
- Data proficient
- Data savvy, and
- Data driven
4. Data Quality Management
Data quality management is a crucial component of any enterprise data strategy. This is especially true when it comes to big data analytics. Accurate and perceptive analysis depends on high-quality data. The primary components that determine data quality are accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness. Big data analytics can suffer from poor data quality since it might produce incorrect or irrelevant insights, which can cause a company to lose a lot of money.

5. Information Architecture Systems
Systems for information architecture are used to store and manage enormous volumes of data, including data lakes, data warehouses, and data marts. The systems' essential building blocks, data standards, and governance provide accurate, dependable information. Organizations can increase their capacity to glean insights from their data by putting in place an information architecture system.
6. Data Integration Process
Data integration, which entails merging data from diverse sources into a cohesive picture, is a crucial stage in an enterprise data strategy. Data profiling, the first step in the procedure, involves examining the data to comprehend its quality, structure, and substance. The process of transforming data into a format that is standardized and acceptable for analysis comes next. All the modified data are finally combined for analytics through data consolidation.
7. Data Analytics Capabilities
Several data analytics capabilities that can aid companies in making sense of huge data can be enabled by an enterprise data strategy. In order to enable effective reporting and decision-making processes that may have an impact on company outcomes, data must be effectively used. The data analytics lifecycle and strategy include undertaking readiness and risk assessments, choosing analytics and reporting tools to match corporate goals, and identifying and tracking technical usage metrics.
8. Design Data Frameworks
A key component of developing an enterprise data strategy is designing data frameworks. An organization's ability to create a solid foundation for using data as a strategic asset is aided by a well-designed data framework. When creating data frameworks, a number of important factors, such as data governance, data architecture, data modeling, and data integration, must be taken into account. In order to ensure that the strategy is in line with business objectives, collaboration between IT and business teams is essential while creating data frameworks.
9. Information Silos
When separate teams interpret data in different ways, information silos emerge, which results in inconsistent reporting and inaccurate data. As a result, it is challenging to believe the facts and draw insightful conclusions. By introducing governance and standardization, establishing a common language, and preventing data from being segregated, an enterprise data strategy (EDS) can assist in eliminating these silos. EDS also makes a distinction between the two types of architecture.
10. Data Stewardship Activities
An enterprise data strategy must include data stewardship initiatives, too. They involve overseeing the quality, integrity, and security of data throughout its entire lifecycle. Identifying high-value and mission-critical data assets, establishing data governance, and facilitating data sharing across all tiers of government are some specific examples of data stewardship activities. By ensuring that the data utilized for analysis is trustworthy and pertinent, these actions help big data analytics succeed within a company.
Start building with a free account
Frequently Asked Questions
To create an effective data strategy, you should first identify key strategic initiatives and programs while incorporating the enterprise data strategy into them. Then, you need to formalize the strategy into a data strategy document that organizes processes and methodologies for each key data activity. Next, define an effective program management organization that tracks the delivery of new capabilities. Finally, make sure your data strategy goals support your organization's overall business strategy.
Since it guarantees data security and integrity, data governance is a crucial part of an enterprise data strategy. It explains the procedures, rules, and requirements for efficient data management throughout the life cycle and specifies who is permitted to take what action. An enterprise data strategy outlines how a company leverages its data to accomplish its technology as well as business objectives and create a competitive edge.
Large-scale data analysis is the procedure used to find patterns and come to wise conclusions. It entails the use of tools and methodologies to extract useful information from data. Plus, it can assist companies in recognizing trends, patterns, and growth prospects. Effective data analytics require a solid data strategy because it offers a framework for gathering, storing, and analyzing data in a consistent and secure manner.
There are a few key considerations to keep in mind, including:
- Type and volume of data: Enterprises need to consider both the type and amount of data they are collecting and storing.
- Scalability and accessibility: Enterprises need to choose a storage solution that can scale as their data needs grow.
- Cloud vs. Edge storage: Cloud storage offers scalability and accessibility, while edge storage enables data to be processed closer to the source.
- Data security and compliance: Enterprises must ensure that their chosen storage solution meets their security and compliance requirements.
These factors impact the storage solution companies choose, which is crucial for an effective enterprise data strategy. Make sure your data is stored in a way that supports your business goals.
To create an effective enterprise data strategy, there are several tools that must be utilized.
- The first tool is to identify key existing or planned strategic initiatives and programs before incorporating the data strategy.
- Next, you need to start with use cases.
- The third tool is to evaluate potential data use cases through different lenses, from improving evidence-based decision-making to understanding customers and markets and improving internal processes.
- Finally, you should have control mechanisms in place to ensure that the data strategy is implemented effectively.
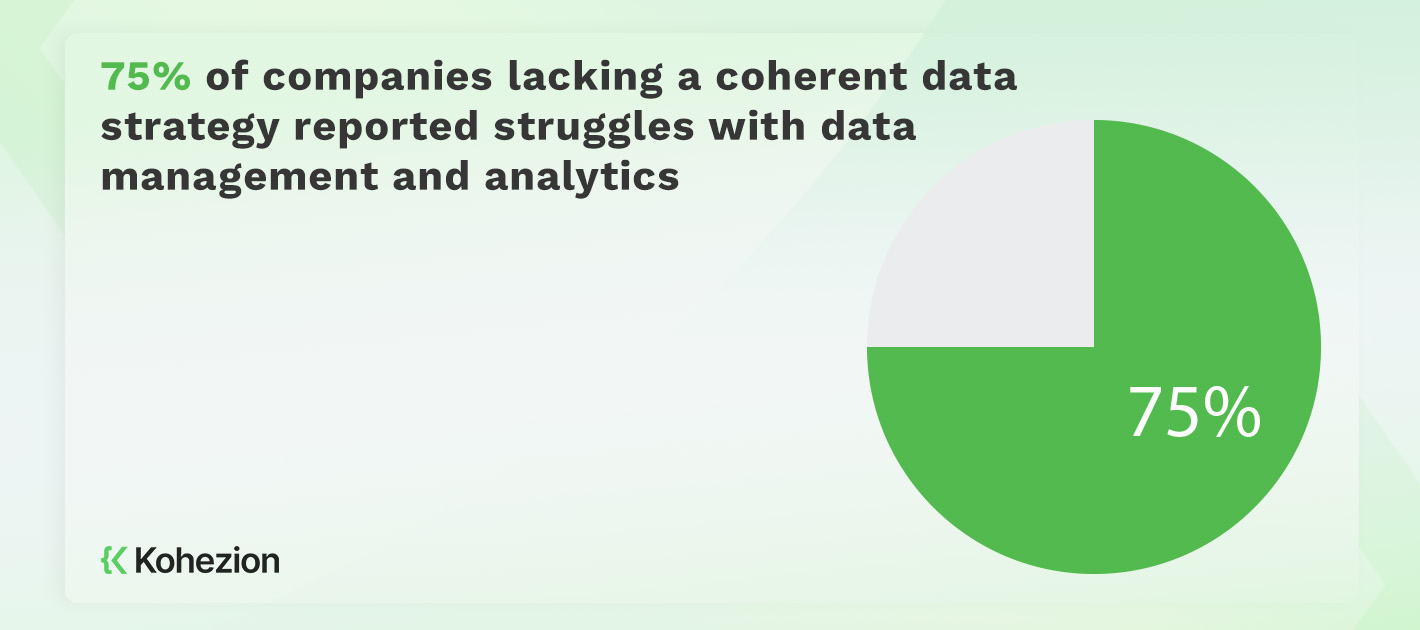
Some common challenges include data quality, accessibility, and integrity. Let's start with data storage and ingestion. It can be challenging, especially when dealing with unstructured data. Companies may also have trouble managing master data and using datasets. Another difficulty is ensuring accurate reporting and retrieval. Unstructured data may also be challenging for companies to integrate into their strategies, which can lead to missed opportunities. Building a roadmap for carrying out and operationalizing the strategy requires careful consideration of timing and sequencing, which can be quite challenging as well.
By offering a clear structure for gathering and evaluating data to support business choices, an enterprise data strategy can significantly improve decision-making processes. Data can be used to enhance evidence-based decision-making, provide smarter goods/services, and enhance internal processes by identifying key data use cases that are in line with the strategic goals of the organization. Likewise, manufacturing companies can use data to optimize their production processes and reduce waste.