Master Data Management (MDM) systems help organizations effectively manage their data assets. According to Gartner, organizations utilizing MDM software have experienced a potential improvement of up to 20% in data accuracy, coupled with a 15% increase in organizational efficiency.
This article will explore examples, benefits, practices, software, and MDM tools to help you understand how MDM can streamline your data management processes and drive business success.
What is Master Data Management?
The goal of master data management (MDM) is to guarantee the accuracy and consistency of shared data inside an organization. For example, important commercial information about clients, goods, and suppliers.
Eliminating data silos, cutting down on duplication and missing data, and creating a single source of truth for all crucial data are the main objectives of MDM implementation. A large retail company using MDM to manage product information from many sources to assure the integrity and consistency of product data across all sales channels and touchpoints is a real-world example of MDM in action.
Many big companies (like Coca-Cola, Johnson & Johnson, and GE) have effectively deployed MDM to improve their decision-making procedures. These companies have benefited from their MDM projects in terms of better data quality, greater efficiency, and better decision-making.
What is a Master Data Management System?
A master data management system (MDM) is like a central hub for important information in a company. It helps keep things organized and consistent, like customer details or product information. MDM systems keep everything in one place, making it easier for businesses to make decisions and work efficiently.
They can bring together different types of data from across the company, helping everyone see the big picture. MDM systems are key for businesses to stay organized and make good choices.

Why is Having a Master Data Management System Important?
Having a master data management system is important for businesses because it helps keep all their important information organized and consistent. Having different versions of customer details or product information scattered across different systems can be confusing and lead to mistakes.
With an MDM system, everything is kept in one place, making it easy for everyone in the company to access the same accurate data. This means better decision-making, smoother operations, and happier customers. So, having an MDM system is crucial for businesses to stay organized and run smoothly.
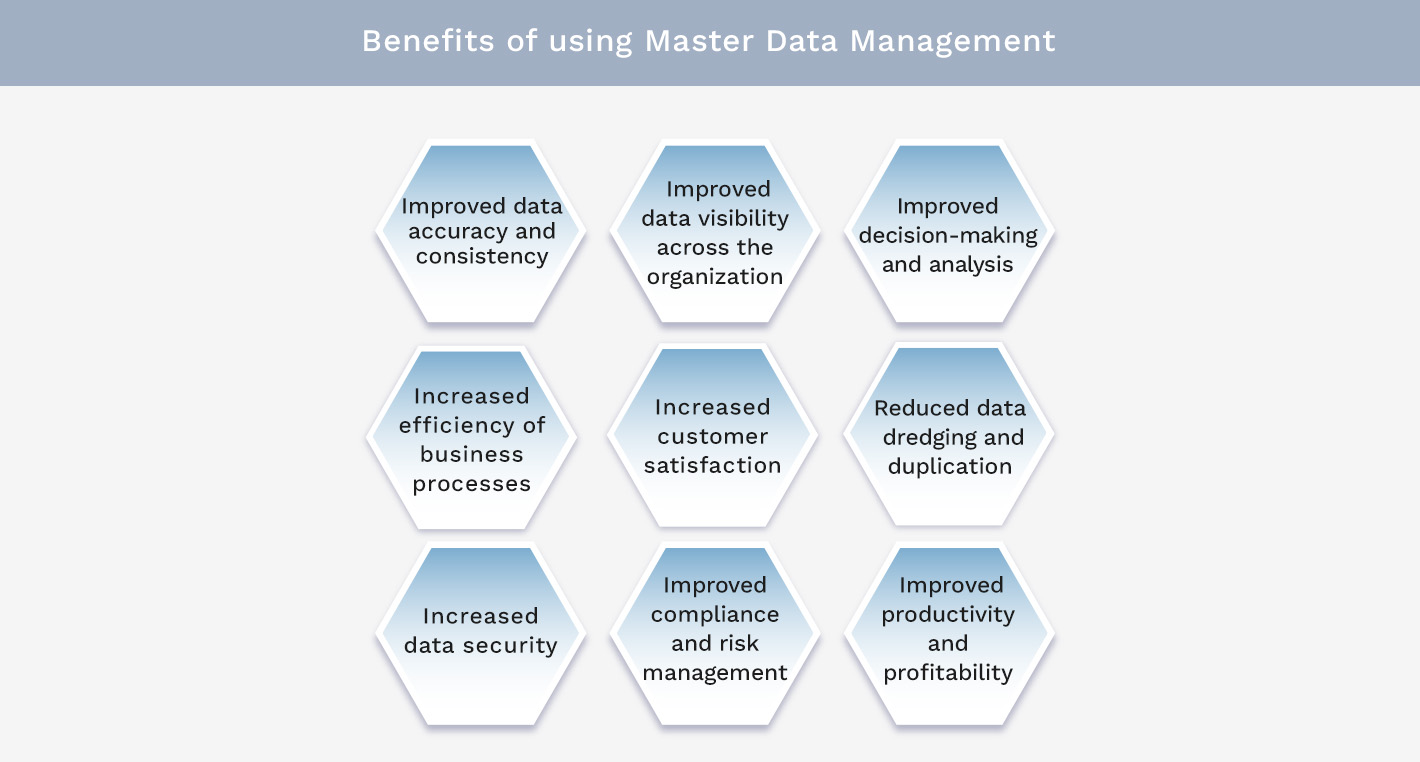
Benefits of using Master Data Management
Implementing MDM has many benefits, from improved data quality and better reporting to streamlined data sharing between business systems and more trustworthy data for business intelligence and analytics applications. Here’s a full list:
1. Improved data accuracy and consistency
MDM helps create procedures and tools for managing crucial data at scale, increasing data consistency and accuracy. Reduce errors and redundancy by removing redundant and contradictory information with MDM. That's not all. It also centralizes and manages mission-critical data, increasing productivity and fostering trust in the data.
2. Improved data visibility across the organization
MDM offers a single point of reference for crucial data, which can significantly increase data visibility throughout an organization. Regardless of where the data originated, MDM ensures everyone in the business has access to correct and current information.
3. Improved decision-making and analysis
A single, accurate, consistent picture of vital business data can be created through the master data management (MDM) process. Information on customers, products, and vendors may be included in this data.
4. Increased efficiency of business processes
Master Data Management (MDM) can increase the efficiency of business processes in different ways. Basically, this can be achieved by improving data quality, reducing errors, and eliminating information silos.
Improving master data quality will result in higher efficiency. Organizations can also save time and resources with automated and optimized data operations, hastening the introduction of new goods and services.
5. Increased customer satisfaction
Master data management can significantly increase customer satisfaction by offering individualized interactions and delivering a consistent experience across channels.
6. Reduced data dredging and duplication
No one likes data dredging and duplication. Repeatedly searching and collecting the same data from different sources results in redundant and conflicting information. This is where Master Data Management (MDM) comes in. It can help reduce data duplication by establishing a centralized and complete master data source.
7. Increased data security
MDM offers more controlled, secure self-service access to trustworthy data. The healthcare, financial, and retail sectors are just a few industries that can take advantage of this benefit. MDM, for instance, can assist in ensuring the accuracy and security of patient data in the healthcare industry and fraud prevention and regulatory compliance in the financial industry.
8. Improved compliance and risk management
Through centralized and complete master data, users (companies and organizations) can reduce costs associated with compliance reporting and penalties.
Mandatory compliance reports and audits help mitigate the risks associated with non-compliance.
9. Improved productivity and profitability
Most importantly, Master Data Management Systems can greatly improve businesses' productivity and profitability by providing a centralized system for managing critical data across different departments and systems.
Example: Procter & Gamble (P&G) has implemented MDM to address its challenges with managing its vast amounts of product data, including information on ingredients, packaging, and labeling across its various brands and regions.
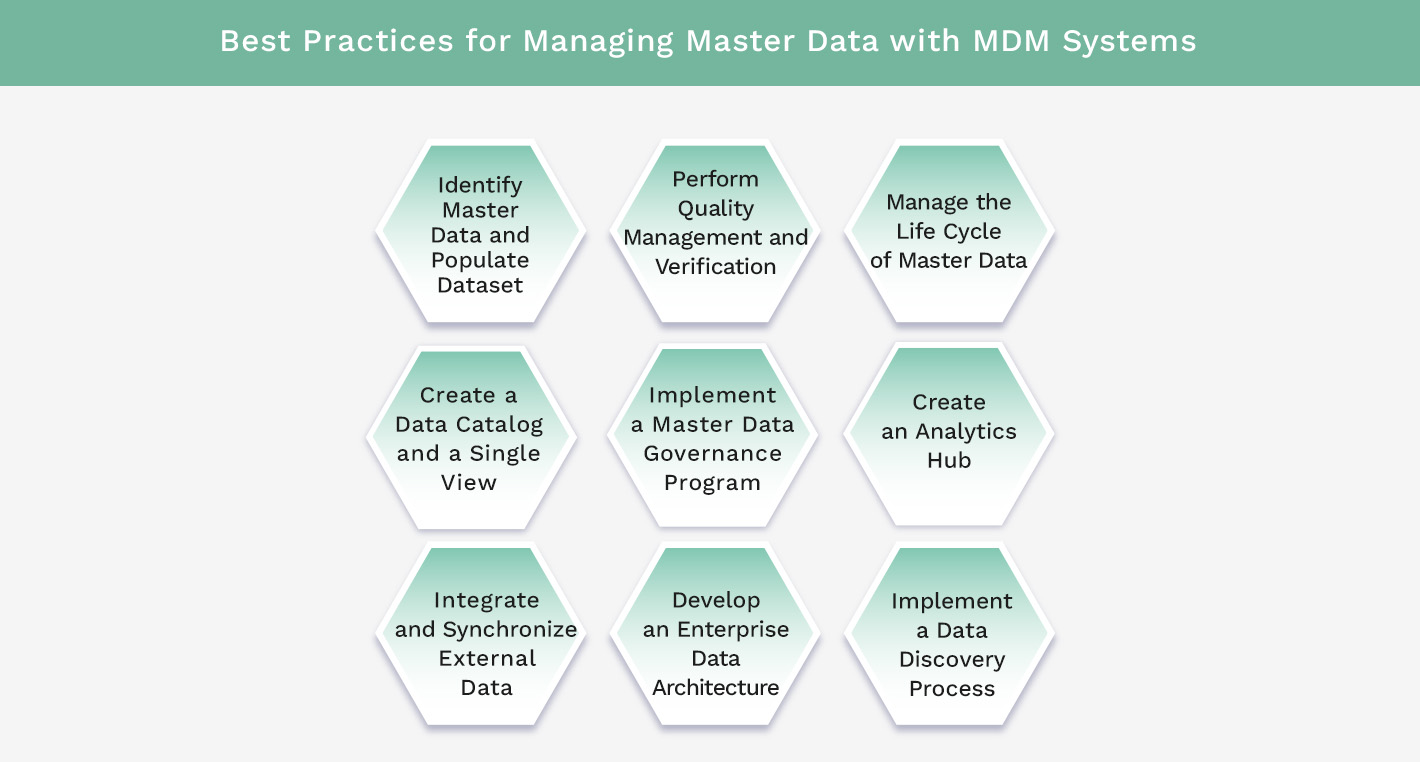
Best Practices for Managing Master Data with MDM Systems
Now that you know the benefits of using Master Data Management, you might want to know how to get the most out of MDMN tools. Let's dive:
1. Identify Master Data and Populate Dataset
When using MDM tools, the process begins with identifying datasets through several phases, including data profiling, mapping, and cleaning. Data profiling helps determine the accuracy and completeness of the data, while data mapping identifies correlations between various data items. Data cleansing ensures that the data is correct and consistent.
A structured approach to identifying master data involves defining business requirements and identifying data sources, performing data profiling to uncover data quality issues, mapping data elements to recognize relationships between data sources, and cleansing the data for accuracy and consistency. Stakeholders should be involved in validating master data attributes, populating the master dataset, and establishing ongoing data governance processes to maintain data quality and consistency.
2. Perform Quality Management and Verification
Quality control and verification prevent costly errors and inconsistencies. MDM tools offer features such as data consolidation, governance, quality management, and proactive monitoring.
3. Manage the Life Cycle of Master Data
The life cycle stages where MDM tools can be beneficial include creation, maintenance, and retirement. During the creation stage, databases and applications containing data for the master record are identified, and all attributes or characteristics of the data are defined, with data being matched, reconciled, and merged as necessary.
In the maintenance stage, new data is cleansed, transformed, and integrated into the master list to maintain consistency and quality of records, with MDM tools automating and accelerating many aspects of this process. During the retirement stage, outdated or irrelevant data is removed from the master list, with MDM tools aiding in identifying and retiring data that is no longer needed.
4. Create a Data Catalog and a Single View
A data catalog should be designed to provide a consolidated view of all master data to allow for easier data discovery and understanding. For this purpose, many companies use MDM tools like Microsoft's Azure Data Catalog, Sphera's Master Data Management, and Pimcore.
These tools offer features for managing master data, including business semantics management, data governance, and data integration.
5. Implement a Master Data Governance Program
Establish a structured framework that defines roles and responsibilities, establishes policies and procedures, and implements a data quality framework. First, locate the apps and databases that house the data that will be part of the master record. The data should be matched, resolved where inconsistent, and merged where numerous records exist.
The application should concentrate on maintaining the initial master data record after creating it by purging, converting, and incorporating fresh data. Utilizing MDM tools that use AI and machine learning may automate this process.
6. Create an Analytics Hub
The best practice for managing master data involves constructing an analytics hub, which necessitates connecting master data from various sources to create a centralized repository. This centralization allows business and IT users to collaborate effectively, achieving a trusted 360-degree view of master data across the organization.
The process begins with identifying all sources of master data within the organization and selecting the appropriate MDM tool. Once the master data is centralized and standardized using these tools, it is integrated into an analytics hub. Customizable dashboards and workflows are then created, utilizing pixel-perfect reports and report formatting templates.
Dynamic data refresh, data sharing, and in-Excel collaboration are implemented to enhance functionality. Mobile access and third-party scheduling reports are also provided, enabling users to access and share data anytime, anywhere.
7. Integrate and Synchronize External Data
MDM tools can also be utilized to integrate and synchronize external data. Yet, integrating external data can be challenging due to data mapping and transformation. Use an MDM tool with data profiling/cleansing and mapping capabilities. Once you have identified the sources of external data and profiled the data, map the data to the MDM model. You can also synchronize the data with the sources.
8. Develop an Enterprise Data Architecture
Establishing a clear data governance framework is important. Include policies, workflows, and roles that ensure data quality and consistency across all applications. Integrating data from diverse sources, such as reference data, metadata, and master data assets, is part of a holistic approach to data management. This method enables a more thorough comprehension of the data and its linkages.
9. Implement a Data Discovery Process
An essential practice for managing master data with MDM technologies involves implementing a data discovery strategy. This process begins with defining the scope of the discovery process and identifying the critical processes and data domains for the organization.
Next, identify data sources and assess their quality, developing data governance policies to ensure effective and secure data management throughout its lifecycle. Collaboration with IT and business stakeholders is crucial to understand their data needs and priorities. Leveraging MDM tools helps automate and streamline the data discovery process, improving efficiency and accuracy.
MDM Systems and Their Features
Below, we provide an overview of different MDM systems and their key features. We outline the functionalities offered by each system, helping readers understand the capabilities and benefits of various MDM solutions.
1. Kohezion
Kohezion is an online database platform that can be used as a master data management system. It can guarantee the accuracy and consistency of shared data inside an organization. Kohezion gives businesses the tools they need to develop web applications with more encryption and security, and users can create data applications.
Kohezion can act as a Master Data Management system, system of record, Business Management Software, Non-Profit CRM, Clinical Data Management System, and Compliance Management Software.
Kohezion provides a simple, low-code solution (actually a database builder) that lets organizations be independent of developers while empowering them to focus on other activities and be more efficient.
Top 5 Features:
- Customizable database applications.
- Real-time collaboration tools.
- Automated workflows.
- Reporting and analytics features.
- Secure cloud storage.
Benefits:
- Improved data accuracy.
- Improved team collaboration.
- Streamlined workflow processes.
- Valuable insights from analytics.
- Secure data storage and access.
Cons:
- Limited integration options with other software.
- A steeper learning curve for new users.
Best For: Large businesses looking for customizable database applications and streamlined collaboration tools without the complexity of larger MDM solutions.
2. Microsoft MDM
Microsoft offers a Master Data Management (MDM) solution called Master Data Services (MDS). The web-based MDS application allows an organization to manage its master data in one place. Semantic reconciliation facilitates the worldwide identification, linkage, and synchronization of master data across heterogeneous data sources. This process also creates and maintains a central, persistent system of record or index of record for master data.
Top 5 Features:
- Integration with Microsoft products.
- Data governance and security features.
- Scalability for large enterprises.
- Advanced reporting and analytics.
- Hybrid deployment options.
Benefits:
- Seamless integration with existing Microsoft infrastructure.
- Robust data governance and compliance.
- Scalability to manage large datasets.
- Insights-driven decision-making with advanced analytics.
- Flexibility with hybrid deployment options.
Cons:
- Higher licensing costs for advanced features.
- Complex setup and configuration process.
Best For: Enterprises that have already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem and are seeking comprehensive data governance and integration capabilities across their organizations.
3. Informatica MDM
Informatica MDM solution offers a single view of data from various redundant and incompatible sources. It includes data integration, business process management, data security, and AI and machine learning capabilities. Informatica MDM integrates a range of data types, including transactional and supplier data, and enables different domain MDM.
It can be installed on-prem or in the cloud. While its data governance features may be less developed than those of other MDM solutions, it nonetheless offers a highly efficient solution that may improve data management.
Top 5 Features:
- Data modeling and mapping capabilities.
- Data quality management tools.
- Multi-domain support.
- Real-time synchronization.
- Master data governance features.
Benefits:
- Unified view of master data across domains.
- Improved data quality and consistency.
- Real-time data synchronization for accuracy.
- Improved governance and compliance.
- Increased operational efficiency.
Cons:
- A steeper learning curve for advanced features.
- Higher initial implementation costs.
Best For: Enterprises with complex data requirements requiring advanced data modeling, quality management, and governance features across multiple domains.
4. Stibo Systems MDM
Stibo Systems offers a complete set of Master Data Management technologies to assist enterprises in connecting, governing, enriching, and syndicating data across domains. The Multidomain product integrates data across the enterprise, applications, and systems and consolidates master data from many sources into one source. STEP, the company's MDM solution, provides multi-domain MDM for data on products, customers, assets, suppliers, employees, references, and locations.
However, Stibo Systems' MDM system has some downsides, such as a convoluted approval process for processes, a lack of proactive data governance, underdeveloped reference data management capabilities, and few possibilities for cloud adoption.
Top 5 Features:
- Centralized data repository.
- Data modeling and profiling tools.
- Workflow automation.
- Multi-domain support.
- Integration with third-party systems.
Benefits:
- Single source of truth for master data.
- Improved data quality and consistency.
- Streamlined business processes with workflow automation.
- Flexibility to manage multiple domains.
- Seamless integration with existing systems.
Cons:
- Limited customization options.
- Complex pricing structure.
Best For: Businesses that need a centralized repository and robust workflow automation to manage master data across diverse domains and integrate it with third-party systems.
5. Reltio MDM
Master data, reference data, transaction data, interaction data, and social data are combined and related into a unified view via Reltio's next-generation Master Data Management platform, which delivers a cloud-native, scalable, and secure solution. Hierarchies, Connected Graphs, Progressive Stitching, Identity Resolution, Data Quality, Dynamic Survivorship, Universal ID, and Data Governance capabilities are some of its key characteristics.
Top 5 Features:
- Big data architecture.
- Machine learning capabilities.
- Real-time data updates.
- Data-driven applications.
- Scalability for large datasets.
Benefits:
- Advanced analytics with machine learning.
- Real-time data updates for accuracy.
- Customizable data-driven applications.
- Scalability to handle large volumes of data.
- Improved decision-making with actionable insights.
Cons:
- Higher initial setup and implementation costs.
- Requires skilled resources for configuration and maintenance.
Best For: Enterprises leveraging big data and machine learning technologies to manage real-time data updates and drive actionable insights for data-driven applications.
6. Oracle MDM
Oracle's master data management products facilitate the organization, governance, and sharing of master data within the company. Unlike legacy systems, Oracle's cloud-based MDM solutions were created specifically to handle today's complex business models and products.
Top 5 Features:
- Data governance and security.
- Data quality management.
- Multi-domain support.
- Scalability for enterprise-level deployments.
- Integration with Oracle applications.
Benefits:
- Robust data governance and compliance.
- Improved data quality and consistency.
- Unified view of master data across domains.
- Scalability to meet enterprise-level requirements.
- Seamless integration with Oracle ecosystem.
Cons:
- Higher licensing costs for enterprise features.
- Complex setup and configuration process.
Best For: Large enterprises with extensive data governance and scalability needs seeking seamless integration with Oracle applications and comprehensive data quality management features.
Features to Look for in MDM Systems
When selecting a Master Data Management (MDM) system, it's important to focus on key features. Look for data integration, quality management, a centralized repository, scalability, and user-friendly interfaces to ensure effective data management for your business.
Data Integration
This feature ensures that the system can gather and merge different types of data from different sources within your organization. For instance, customer details stored in one system and product information in another can be brought together seamlessly. With effective data integration, your MDM system becomes a centralized hub where all essential data is consolidated, providing a comprehensive view of your business operations.
Data Quality Management
Data quality management tools are designed to maintain the accuracy and cleanliness of your data. They identify and rectify inconsistencies, errors, and duplications, ensuring that the information stored in your MDM system is reliable and trustworthy. Upholding high data quality standards helps businesses make informed decisions based on accurate information, improving efficiency and effectiveness.
Centralized Repository
An MDM system is a central repository for all your critical data, storing it in one accessible location. This centralized approach eliminates searching for specific information through multiple systems or departments. Instead, employees can easily locate and access the data they need from a single source, streamlining workflows and promoting collaboration across the organization. A centralized repository ensures that everyone works with the same up-to-date information, fostering consistency and alignment within the company.
Scalability
A scalable MDM solution can accommodate increasing volumes of data and users without sacrificing performance or functionality. As your business expands, your MDM system should be able to scale up seamlessly to meet the growing demands, ensuring continued effectiveness and efficiency. Choosing a scalable MDM system helps you future-proof your data management infrastructure and avoid the need for frequent system upgrades or replacements.
User-Friendly Interface
A user-friendly interface makes it easy for employees at all levels to navigate the system and access the necessary information. Intuitive features and straightforward navigation menus minimize the learning curve, enabling employees to quickly familiarize themselves with the MDM system and start using it effectively. A user-friendly interface promotes productivity and engagement, as employees can focus on tasks without being hindered by complex or confusing software interfaces.
Use Kohezion for Master Data Management
Kohezion is a straightforward, user-friendly solution for organizing and managing crucial data assets. With its customizable database applications and real-time collaboration tools, Kohezion empowers businesses of all sizes to centralize their master data, ensuring accuracy and consistency across the organization.
Kohezion offers features to streamline your data management processes and drive better decision-making, from data modeling to workflow automation. Whether you're tracking customer information, inventory data, or project details, Kohezion provides a reliable platform to keep your master data organized and accessible.
Conclusion
Mastering data management helps businesses ensure data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility across their organization. Implementing the right MDM system helps businesses streamline their data management processes, improve decision-making, and drive better business outcomes.
Whether you choose Kohezion or another MDM solution, evaluating your specific needs and requirements is essential to finding the best fit for your organization. If you want to learn more about how Kohezion can help streamline your data management processes, please contact us.
Start building with a free account
Frequently Asked Questions
Several MDM software categories are used, including data integration, quality, and governance tools. Data integration tools (like SnapLogic) unite disparate data while creating high-quality master data reference sources using data science and machine learning. Data quality tools (e.g., Talend) ensure accurate, consistent, and standardized data. As for the data governance tools, they provide a framework for managing the policies and processes for enterprise data. Or, use one single source of truth like Kohezion’s online database to avoid needing multiple MDM categories.
Data management involves gathering, arranging, and making all data inside an organization accessible. One type of data management, master data management (MDM), focuses on the characteristics of key business entities such as clients, vendors, products, and assets. MDM ensures that all crucial data throughout the organization has a single source of truth.
Master Data Management systems are capable of managing various types of data, including:
- Product data includes information such as product color, size, and materials.
- Location data includes information like zip codes, area codes, and three-letter airport codes used by airlines.
- Customer data includes essential customer information like their names, contact information, and purchase history.
Other data includes reference data, such as healthcare codes used between organizations.
MDM software can collect and organize enterprise data from different sources, including internal and external data sources, legacy systems, and cloud-based systems. Master Data Management systems help connect dispersed data points by acting as a central repository for data management, cleaning, and verification. Thanks to multidomain MDM technologies, organizations may manage all master data on a single, integrated data management platform.

